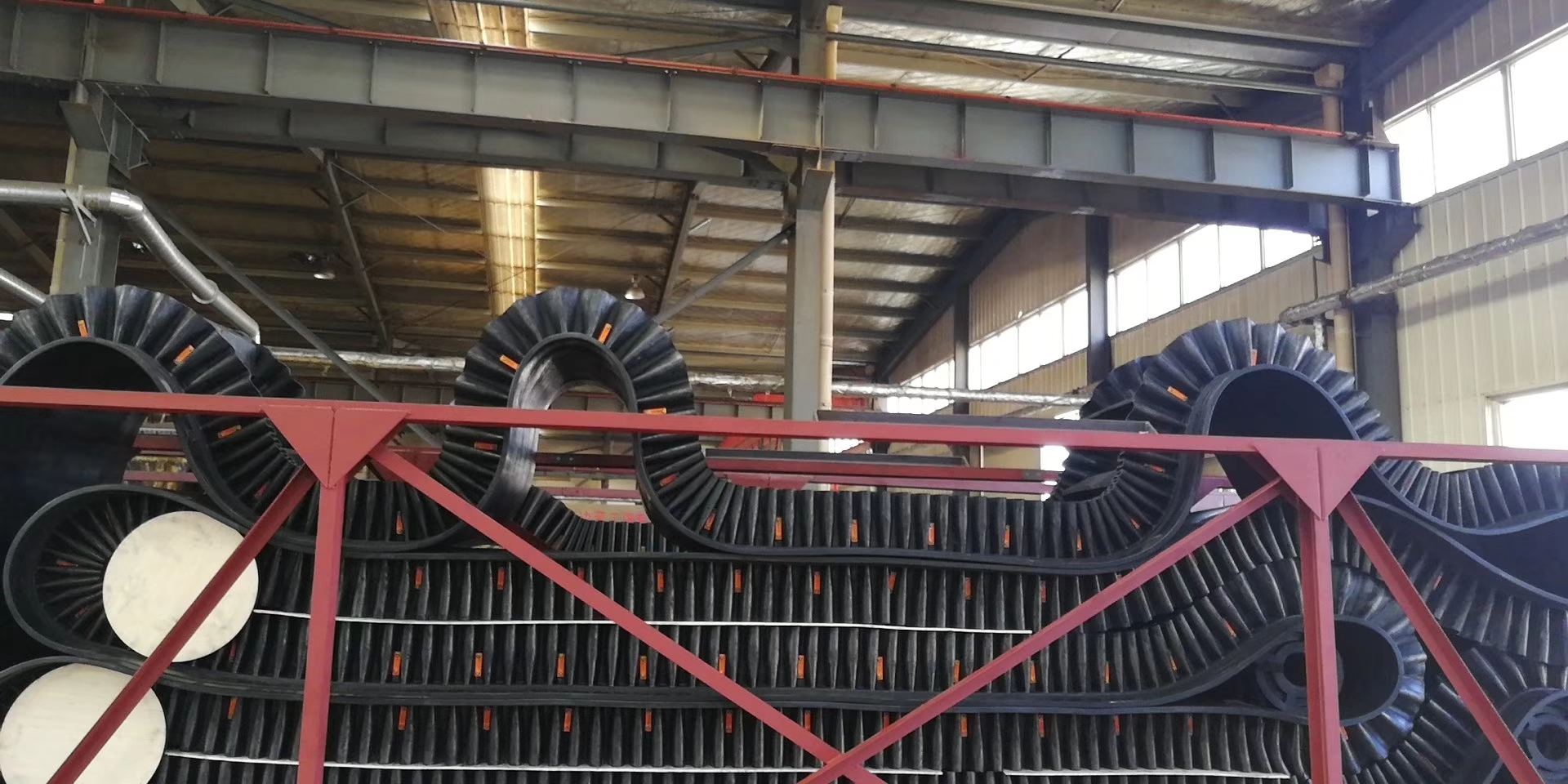
Sidewall Rubber Conveyor Belt Guide: 10 Key Design Considerations
Transporting bulk materials at steep angles with standard conveyor belts often causes material spillage and operational inefficiency. This loss of material drives up your costs, demands more maintenance, and hurts your system’s capacity. This guide shows how specially designed sidewall rubber conveyor belts offer a dependable fix, stopping spillage and optimizing handling even on extreme inclines.
1. What are the fundamentals of sidewall rubber conveyor belts?
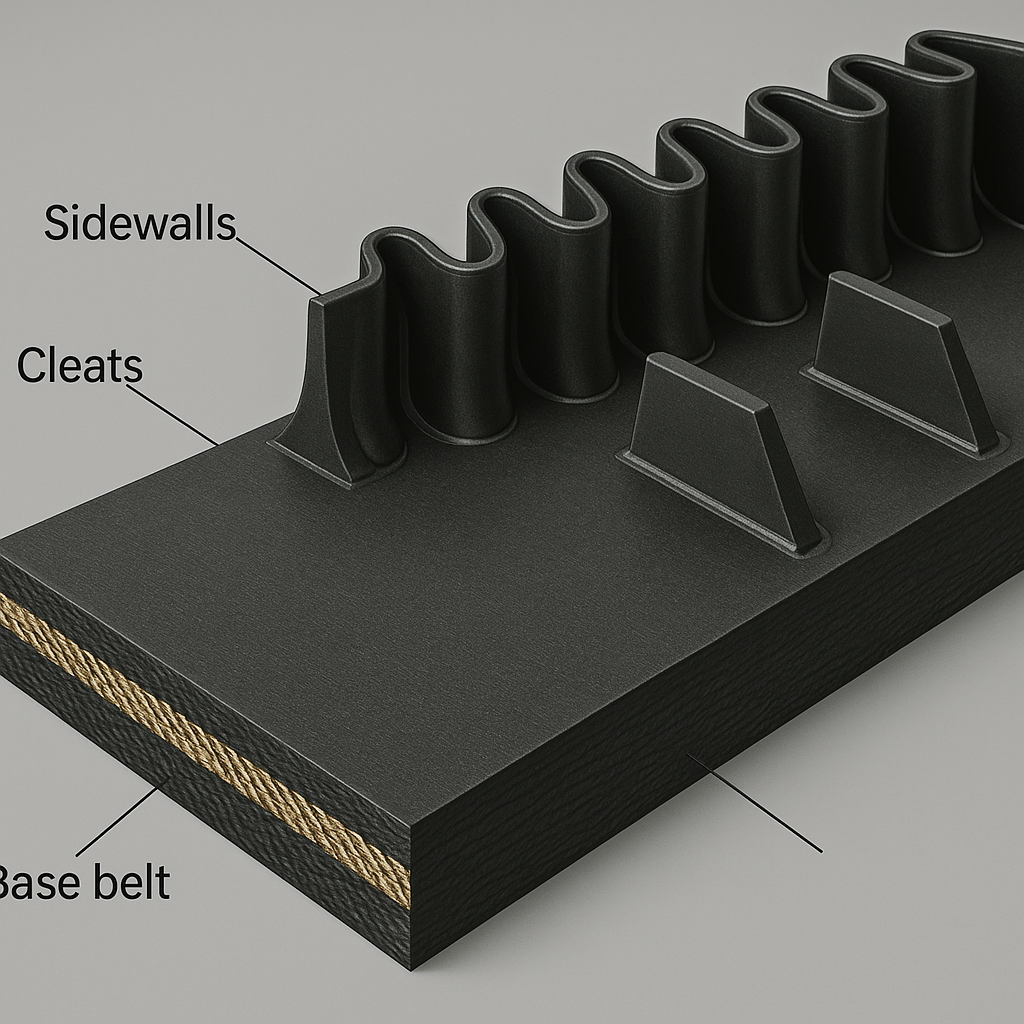
Solving Steep Angle Conveying
Standard conveyor belts struggle with inclines over 18 degrees, leading to material rollback and spillage. Sidewall belts are engineered specifically to overcome this limitation. By creating contained pockets, they can move materials at angles up to 90 degrees, effectively turning a horizontal conveyor into a vertical lift system.
Preventing Bulk Material Loss
The integrated sidewalls and cleats form a pocket-like structure that holds material securely during transport. This design eliminates the spillage common with traditional flat belts, particularly at transfer points or along steep sections. But here’s the real benefit: this containment directly translates into higher efficiency and a cleaner, safer work environment.
Key Takeaway: Sidewall conveyor belts are the specialized solution for steep-angle conveying, using a pocket design to prevent material loss and enable vertical transport.
2. What is the base of a sidewall rubber conveyor belt?
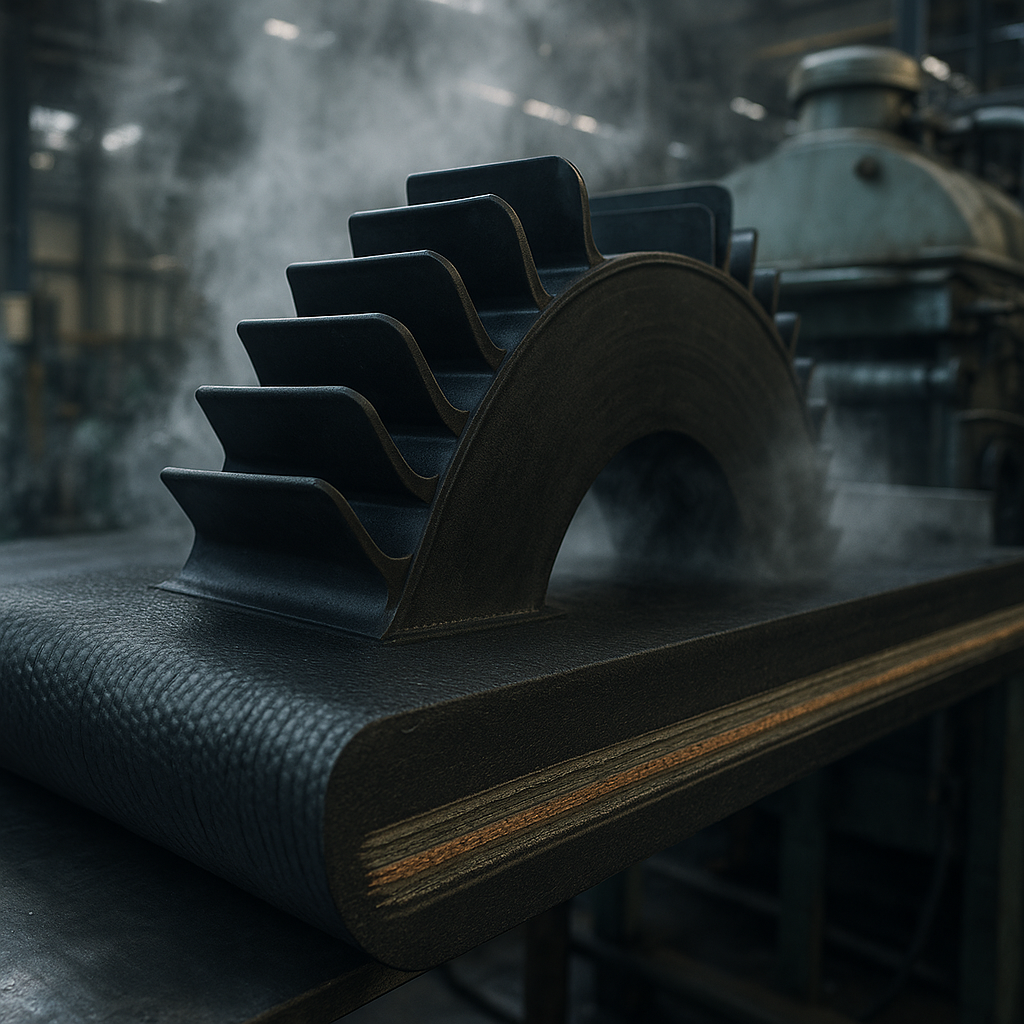
Base Belt Construction
The foundation of any sidewall belt is its base. It must possess high transverse rigidity to prevent sagging between idlers, especially when loaded. This rigidity allows the belt to run smoothly on horizontal guide pulleys and maintain its shape under pressure, which is a deciding element for system stability.
The Hot Vulcanization Process
Sidewalls and cleats are attached to the base belt using a hot vulcanization process. This method creates a powerful, lasting chemical bond that is far superior to simple cold bonding. You might be wondering why that matters. A hot vulcanized bond means the components act as a single, durable unit, capable of withstanding high stress and flexing without separation.
Key Takeaway: A rigid base belt combined with hot-vulcanized components creates a single, durable unit capable of handling heavy loads without failure.
| Component | Function | Manufacturing Process | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Belt | Provides transverse rigidity and structural support | Specialized material layering | |
| Sidewalls | Contain material on the belt | Hot Vulcanization | |
| Cleats | Prevent material rollback on inclines | Hot Vulcanization |
3. What are the carcass types for a sidewall rubber conveyor belt?
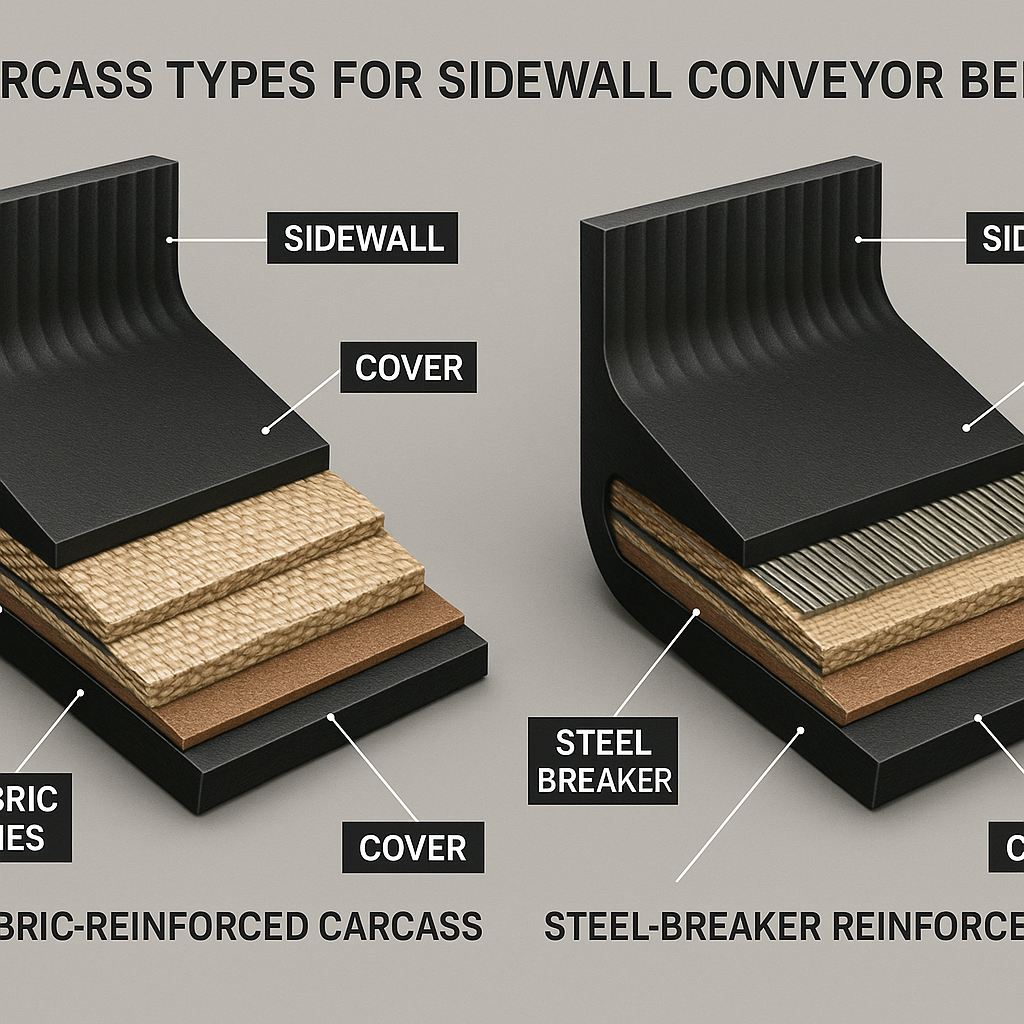
Fabric-Reinforced Carcass
For most applications, a multi-ply fabric carcass using materials like polyester and nylon provides an excellent balance of flexibility and strength. This type offers good transverse rigidity while remaining pliable enough to navigate the conveyor system’s pulleys without damage.
Steel Breaker Reinforced Carcass
When extra rigidity is needed for wider belts or heavier loads, a steel breaker-reinforced carcass is the answer. It incorporates steel cords within the fabric layers, significantly boosting the belt’s cross-rigidity. This is where it gets interesting. This design prevents the belt from collapsing inward under heavy loads, maintaining the pocket shape.
Key Takeaway: Carcass choice depends on load and belt width, with fabric for standard use and steel reinforcement for heavy-duty applications.
| Carcass Type | Best For | Key Feature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric (EP/NN) | Standard loads, moderate widths | Good flexibility and strength | |
| Steel Breaker | Heavy loads, wider belts | Enhanced transverse rigidity | |
| Full Steel Cord | Extreme loads, very wide belts | Maximum strength and stability |
4. What materials are used for sidewall rubber conveyor belts?
Abrasion-Resistant Compounds
For handling materials like rock, sand, or aggregates, a highly abrasion-resistant rubber compound is non-negotiable. These formulas are designed to withstand constant friction and scraping, extending the belt’s service life and reducing the frequency of costly replacements.
Heat and Oil-Resistant Options
In environments like power plants handling hot ash or in facilities with oily materials, standard rubber will quickly degrade. So, what’s the solution? Specialized compounds that resist high temperatures and oil are available, protecting the belt’s integrity and preventing premature failure. Flame-retardant qualities can also be included for safety compliance.
Key Takeaway: The rubber compound must match the material being conveyed—choose abrasion-resistant for rough materials and specialized formulas for heat or oil.
| Rubber Compound | Primary Use Case | |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasion-Resistant | Aggregates, mining, sand | |
| Heat-Resistant | Cement plants, foundries, power plants | |
| Oil-Resistant | Recycling facilities, biomass | |
| Flame-Retardant | Underground mining, tunneling |
5. What are the cleat designs for sidewall rubber conveyor belts?
Understanding C-Type Cleats
C-type cleats are designed for conveying materials at moderate angles, typically up to 40 degrees. Their shape provides effective support for most bulk goods without creating excessive stress on the belt as it moves around pulleys.
Exploring N-Type Cleats
For steeper inclines, often exceeding 40 degrees, N-type cleats are used. Their deeper profile offers superior material support, preventing rollback on very aggressive angles. Here’s the deal: The choice between cleat types directly impacts your system’s maximum conveying angle and capacity. Custom models can also be developed for unique material properties.
Key Takeaway: C-type cleats work for moderate inclines, while N-type cleats are required for steep angles to provide adequate material support.
| Cleat Type | Typical Max Angle | Best For | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-Type | ~40° | General bulk materials | |
| N-Type | >40° | Steep incline applications | |
| Custom | Varies | Unique or fine materials |
6. Why use a corrugated sidewall on a rubber conveyor belt?
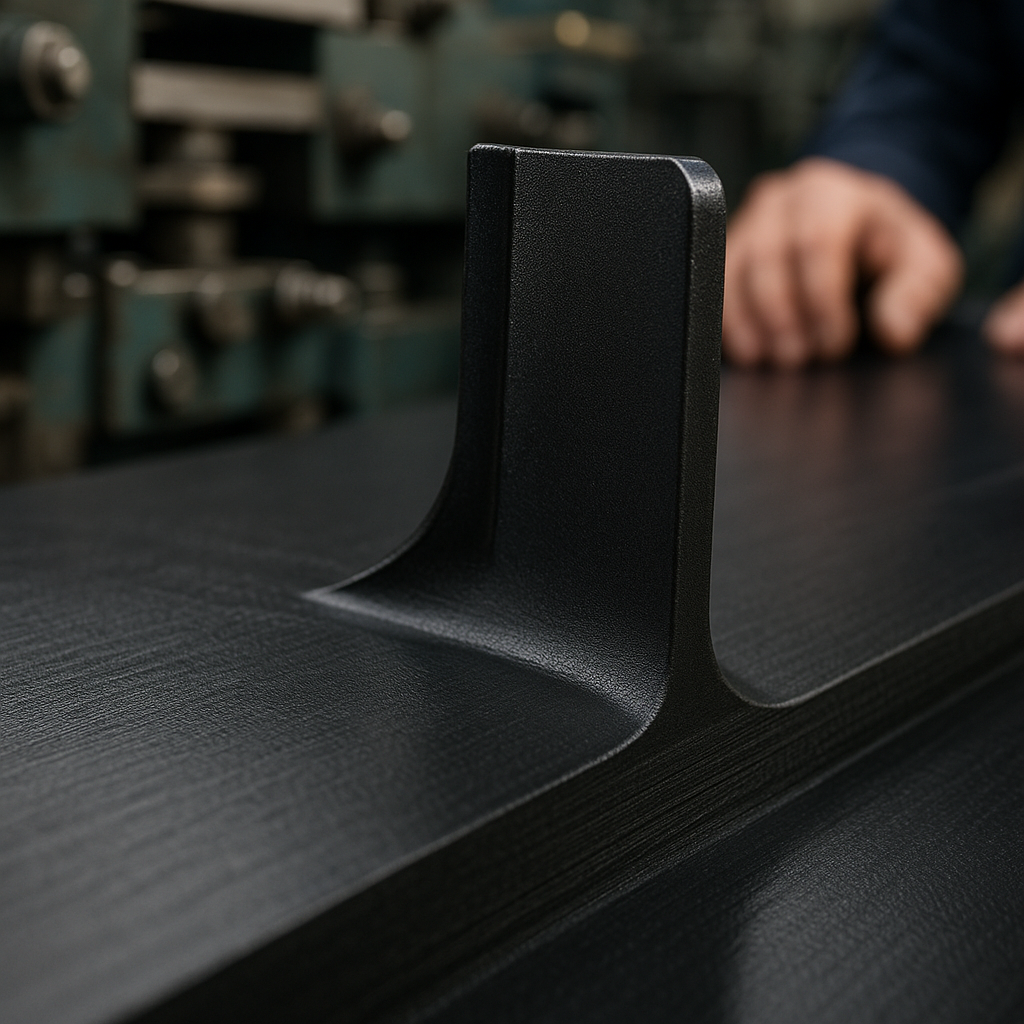

Ensuring Belt Elasticity
A corrugated, or “wavy,” sidewall design is not just for looks; it is a brilliant piece of engineering. This shape allows the sidewall to flex and stretch as the belt travels around the drive and tail pulleys. A straight, rigid sidewall would tear or buckle under this stress.
Preventing Lateral Belt Tearing
The corrugated form absorbs the tension and compression that occurs during deflection. The real story is this: it prevents stress from concentrating at the base of the sidewall, which is a common point of failure in poorly designed belts. This elasticity is a deciding factor for long-term durability.
Key Takeaway: The corrugated design gives sidewalls the necessary elasticity to flex around pulleys without tearing, which is paramount for belt longevity.
| Feature | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Corrugated Profile | Allows sidewall to stretch and compress | |
| High Elasticity | Prevents tearing at deflection points | |
| Stress Absorption | Distributes tension evenly along the sidewall base |
7. How are sidewall rubber conveyor belt specifications determined?

Defining Sidewall Height
Sidewall height, combined with cleat height and belt width, determines the carrying capacity of each belt pocket. This must be calculated based on the volume of material you need to move per hour and the material’s surcharge angle.
Matching Specs to Application
You cannot use a one-size-fits-all approach. Here’s the bottom line: every specification, from sidewall pitch to base belt width, must be tailored to your specific application. Factors include the type of material, required capacity, conveyor angle, and system layout. Consulting with experts is the best way to get it right.
Key Takeaway: Specifications are not arbitrary; they are calculated based on your required capacity, material type, and conveyor design to create a custom solution.
| Specification | Determined By | Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sidewall Height | Material volume, surcharge angle | Carrying capacity | |
| Cleat Pitch | Pulley diameter, material size | Belt flexibility, material containment | |
| Base Belt Width | System layout, capacity needs | Overall system footprint and throughput |
8. What are the advantages of a sidewall rubber conveyor belt?
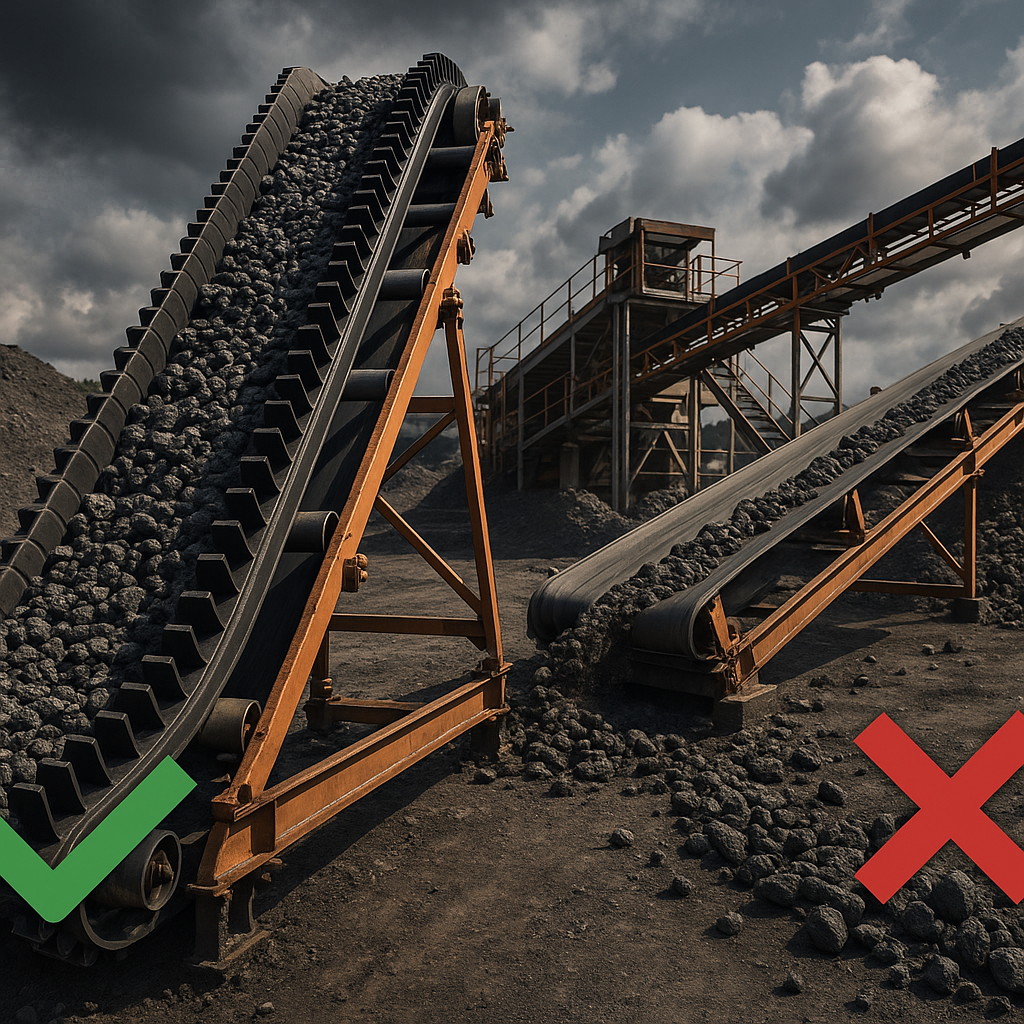

Increased Handling Capacity
By enabling conveyance at steep inclines, these belts can move more material over a shorter distance, often eliminating the need for multiple standard conveyors. This simplifies the system and can dramatically increase your operational throughput.
Low Power & Maintenance Needs
Compared to other vertical conveying systems like bucket elevators, sidewall conveyors have fewer moving parts and require less energy to operate. What does this mean for you? It means lower operational costs, less downtime for maintenance, and a more reliable system day in and day out. The absence of spillage also cuts down on cleanup labor.
Key Takeaway: Sidewall belts offer superior handling capacity, simplified system design, and lower power and maintenance costs compared to alternatives.
| Advantage | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| High Capacity | Achieved through steep angle conveying, simplifying layouts. | |
| No Spillage | Contained pockets prevent material loss and cleanup costs. | |
| Low Power | More efficient than bucket elevators or pneumatic systems. | |
| Reduced Maintenance | Fewer moving parts and less wear lead to greater uptime. |
9. Where are sidewall rubber conveyor belts applied?
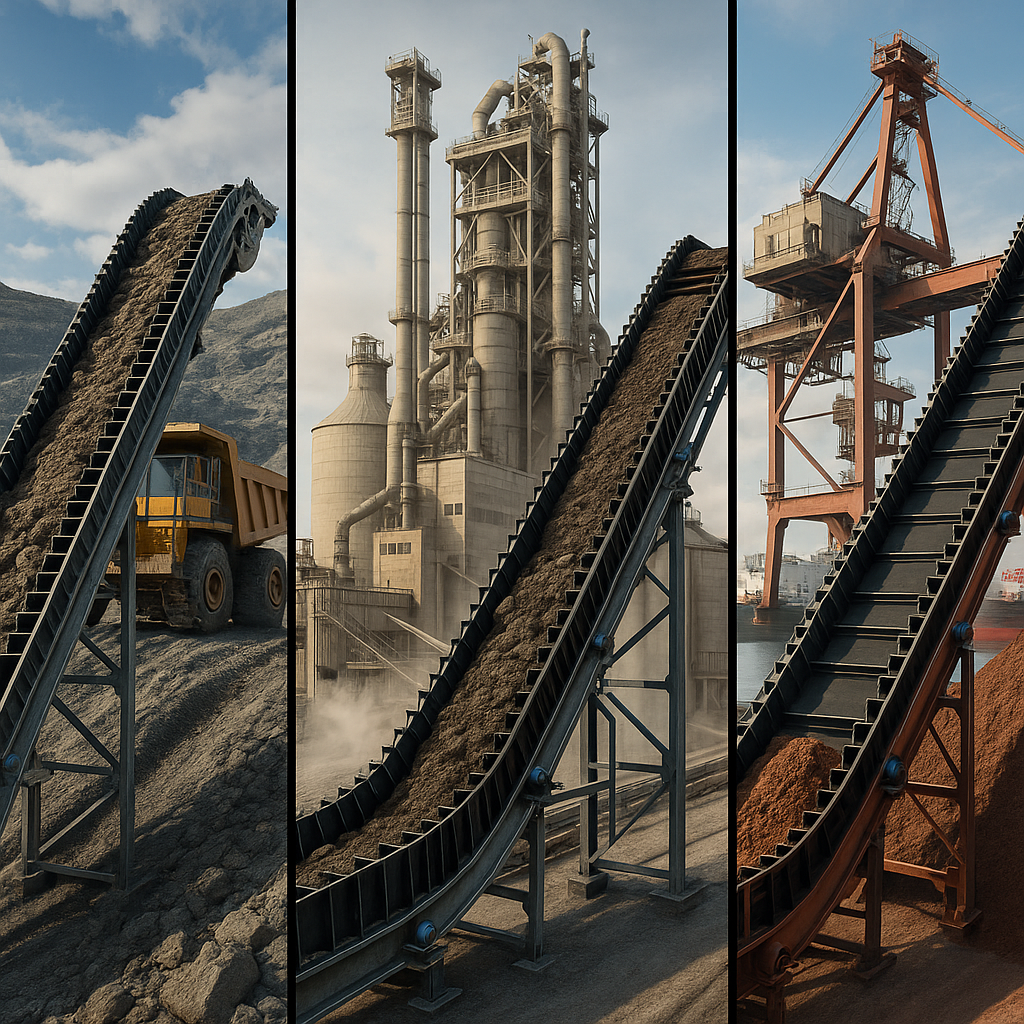

Mining and Tunneling Use
In mining and tunneling, space is often at a premium. Sidewall conveyors are perfect for lifting excavated material vertically out of shafts or moving it up steep inclines within tight confines, where a long, conventional conveyor would be impossible to install.
Cement and Power Plant Use
These industries handle fine, dusty, or hot materials like cement, coal, and ash. The advantage here is clear. The enclosed nature of sidewall belts minimizes dust emissions, creating a safer and cleaner environment while efficiently transporting materials to silos or hoppers at steep angles. Foundries and steel mills also benefit from this for similar reasons.
Key Takeaway: Sidewall belts are used across heavy industries like mining, cement, and power generation where steep, contained, and high-capacity conveying is needed.
| Industry | Common Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Mining/Tunneling | Lifting materials vertically from excavation sites. | |
| Cement Plants | Transporting clinker and other powders up to silos. | |
| Power Plants | Moving coal, wood chips, or ash. | |
| Foundries/Steel | Handling sand, coke, and other raw materials. |
10. How do you choose the right sidewall rubber conveyor belt?
Analyzing Conveyor System Needs
Before anything else, you must have a complete understanding of your system’s requirements. This includes the conveyor length, angle of incline, pulley diameters, and belt speed. These parameters will dictate the necessary base belt construction and component sizes.
Working With Technical Experts
Choosing the right belt involves many variables. But here’s the kicker: you don’t have to figure it out alone. Partnering with technical experts who understand belt engineering is the surest way to get a solution that performs correctly and offers a long service life. They can analyze your needs and recommend the ideal specifications.
Key Takeaway: A successful selection requires a thorough analysis of your system’s technical data and collaboration with belt engineering specialists.
| Selection Step | Action Required | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Analyze System | Document conveyor geometry, speed, and pulley sizes. | |
| 2. Define Material | Specify material type, density, and required capacity (tons/hr). | |
| 3. Consult Experts | Provide data to technical specialists for an optimized belt design. |
Now that you know the key design considerations, you can make a more informed decision for your operation. These belts offer major benefits in capacity, cost, and efficiency. To get a personalized quote for your application, contact our technical department for a direct consultation.
FAQ
Q1: Can I use a sidewall rubber conveyor belt on my existing system? Yes, in many cases, existing conveyor frames can be retrofitted to accommodate a sidewall belt. However, modifications to pulleys and support idlers may be necessary to support the belt’s rigid structure and profile.
Q2: How do I choose the correct carcass type for my needs? The choice depends on your application’s load and belt width. Use a fabric carcass for standard applications and a steel-reinforced carcass for heavy loads or very wide belts to provide the needed transverse rigidity.
Q3: What is the maximum incline angle a sidewall rubber conveyor belt can handle? With the correct combination of sidewall height and cleat design, these belts can convey materials at angles up to 90 degrees (completely vertical).
Q4: Are custom cleat and sidewall sizes available for unique materials? Yes. Sidewalls and cleats can be manufactured in custom heights and designs to match the specific characteristics of your material, such as particle size and flowability, for optimal performance.
Q5: How do maintenance requirements for these belts compare to standard belts? Maintenance is generally lower than for other steep-angle systems like bucket elevators due to fewer moving parts. However, regular inspection of the sidewall and cleat bonding, as well as tracking alignment, remains important.

