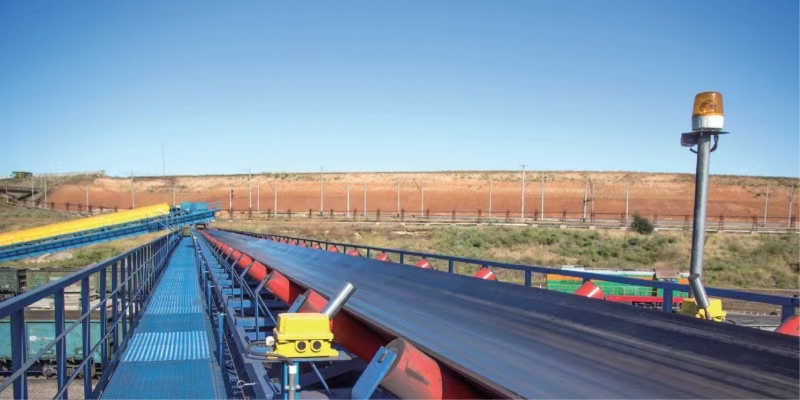
In high-demand industrial settings, constant abrasion and harsh operating conditions often cause belts to fail, creating expensive downtime and lowering overall productivity. Managers face ongoing frustration as unreliable material handling systems interrupt workflow and strain maintenance budgets.
A black rubber conveyor belt provides a dependable solution, engineered for exceptional durability and stable performance even in the toughest environments. Backed by decades of proven results, a high-quality black rubber conveyor belt helps operations run smoothly, efficiently, and with far fewer costly disruptions.
Table of Contents
Understanding Black Rubber Conveyor Belts
You might be wondering how these belts hold up in real-world grit. Black rubber conveyor belts consist of synthetic or natural rubber covers over textile or steel reinforcements, designed for heavy-duty transport. Core composition includes rubber compounds for the outer layer, providing weather and oil resistance, while inner plies offer structural integrity. Durability factors like thickness and reinforcement type determine lifespan, often lasting years in abrasive settings. Historically, these evolved from early 20th-century textile belts to modern steel-cord versions post-WWII, improving load capacities dramatically.
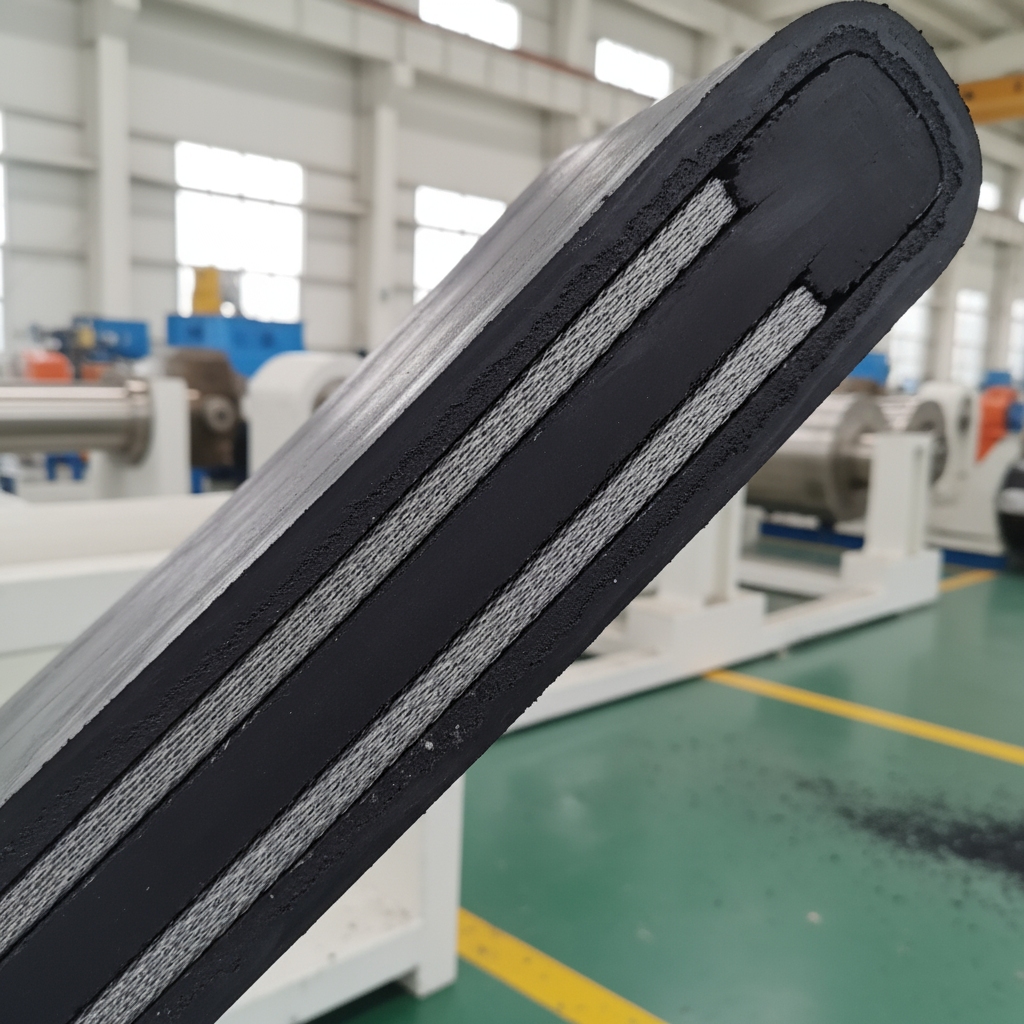

| Component | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Cover | Abrasion-resistant layer | Protects against wear | |
| Textile Plies | Fabric reinforcement | Enhances flexibility | |
| Steel Cords | High-tensile core | Boosts strength |
Black rubber conveyor belts reduce replacement needs by 40% in tough spots.
Key Features of Black Rubber Conveyor Belts
Here’s the deal: Strength and resilience define these belts. Tensile strength varies from 300-2000 N/mm, supporting massive loads without snapping. Abrasion resistance, measured by DIN standards, ensures minimal wear from sharp materials. Flexibility allows bending around pulleys as small as 500mm diameter, vital for curved paths.
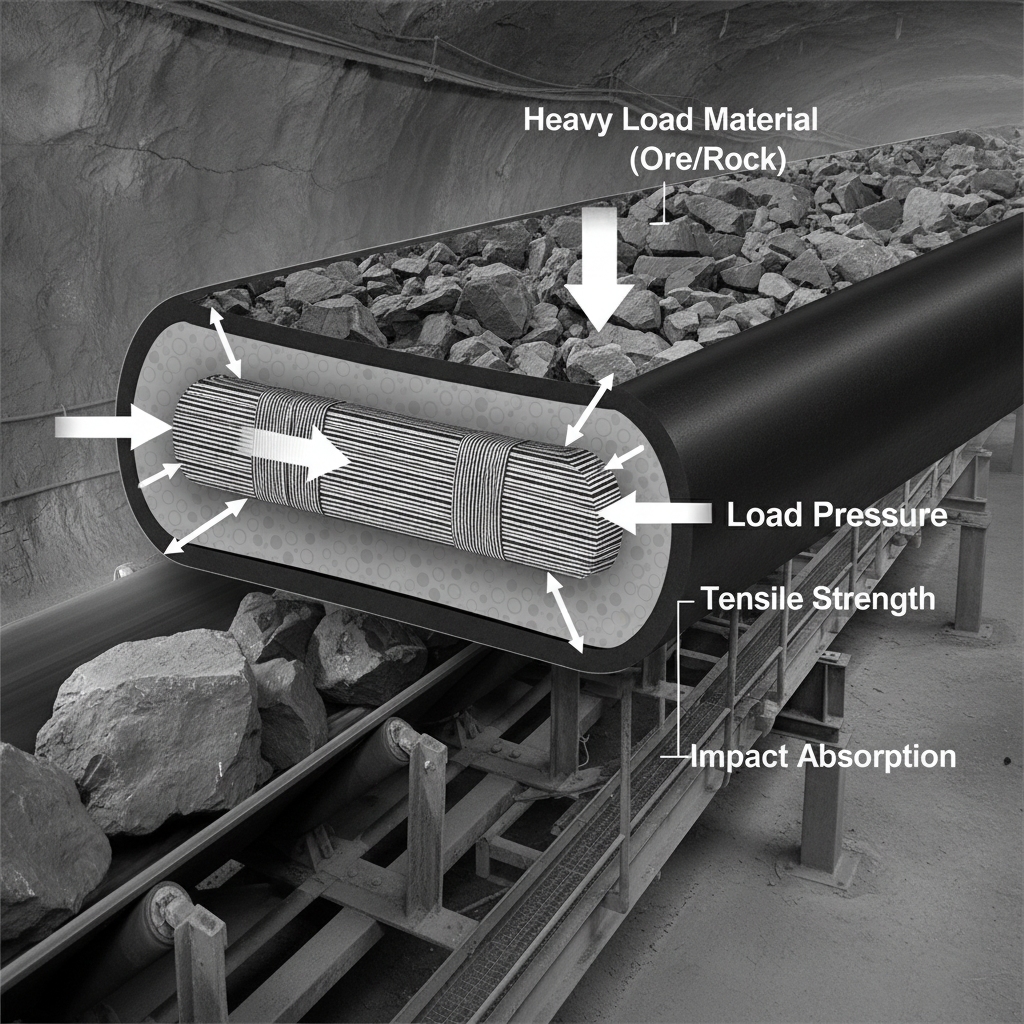
| Feature | Rating | Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 2000 N/mm | Heavy mining | |
| Abrasion Resistance | <120 mm³ loss | Aggregate handling | |
| Flexibility | 500mm min pulley | Inclined conveyors |
These traits integrate smoothly into high-volume setups, lifting throughput.
Types of Black Rubber Conveyor Belts
What’s the catch with variety? Multi-ply textile belts suit moderate loads with 3-5 layers for cost-effectiveness. Steel cord reinforced versions handle extreme tensions, ideal for long distances. Solid woven variants combine fabric and rubber for tear resistance in sharp-material flows.

| Type | Ply Count | Load Capacity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Ply | 3-5 | Up to 500 kg/m | |
| Steel Cord | Single core | 2000+ kg/m | |
| Solid Woven | Integrated | 1000 kg/m |
Right type choice prevents failures under specific loads.
Applications in Mining Operations
Ready for the good part? In ore transport, belts move tons of rock over kilometers, resisting impacts. Coal handling demands dust-proof designs to avoid slippage in wet conditions.
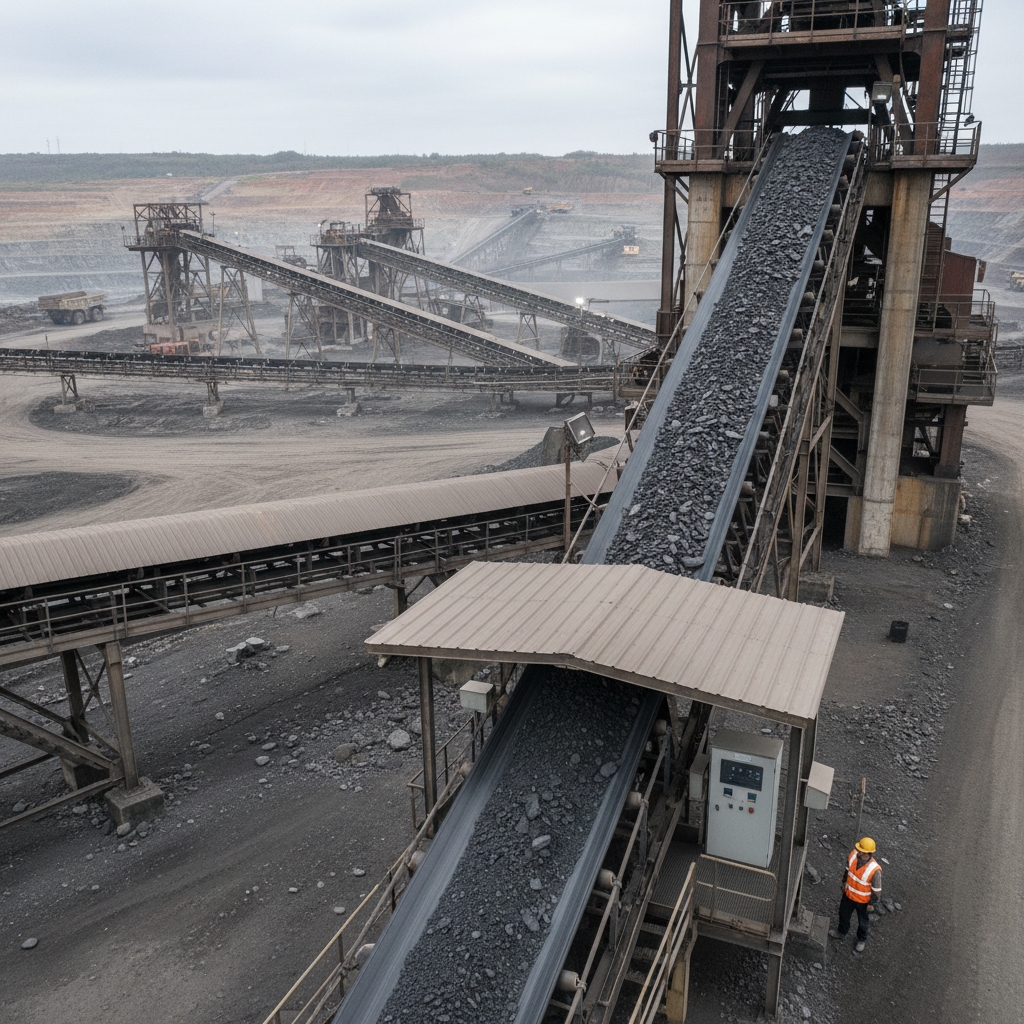

| Application | Load Volume | Efficiency Gain | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ore Transport | 5000 tph | 30% faster | |
| Coal Handling | 3000 tph | Reduced wear 25% |
These belts tackle rough ores without early breakdowns.
Applications in Construction Sites
This is where it gets interesting. Aggregate moving requires belts that grip loose gravel on inclines. Sand and gravel transport needs water-resistant covers for wet mixes.
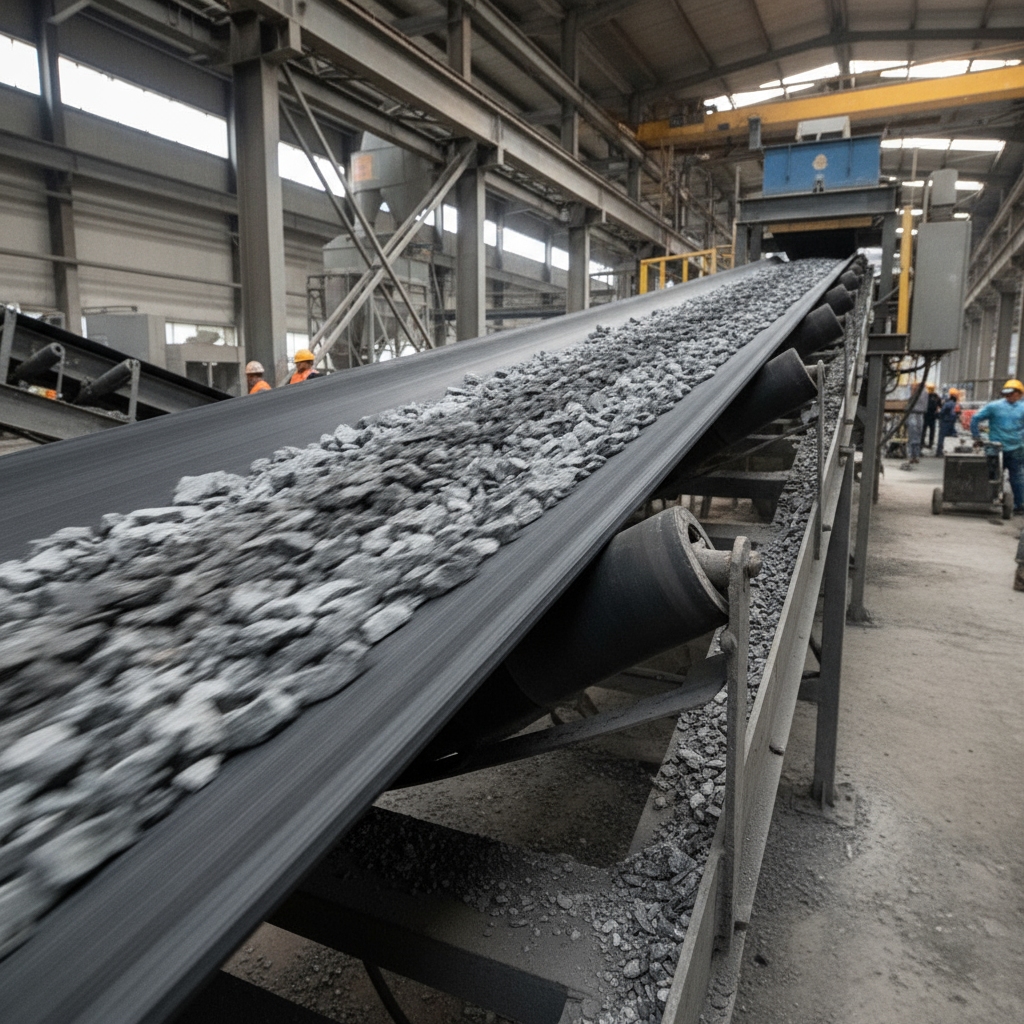

| Application | Terrain Rating | Delay Reduction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregate Moving | High uneven | 40% less | |
| Sand/Gravel | Wet/dry | 35% uptime boost |
Reliable on rough ground, they slash project holdups.
Advantages Over Synthetic Belts
But here’s the kicker. Cost efficiency comes from lower initial prices and longer life. Environmental resilience shrugs off UV and chemicals better. Maintenance stays simple with easy splicing.

| Advantage | Rubber Metric | Synthetic Metric | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | 5x longer | Standard | |
| Cost/Year | $500 savings | Higher upkeep | |
| Resilience | High | Moderate |
Better ROI in harsh spots through endurance.
Installation Guidelines for Black Rubber Belts
You might be wondering about setup ease. Alignment techniques use lasers for straight runs. Splicing methods include hot vulcanizing for seamless joins.

| Step | Tool Required | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alignment | Laser level | Prevent misalignment | |
| Splicing | Vulcanizer | Strong bond | |
| Tensioning | Tension meter | Optimal pull |
Proper steps cut early tensions for steady runs.
Maintenance Best Practices
Here’s the deal on upkeep. Inspection routines check for cracks monthly. Repair techniques patch minor tears on-site. Cleaning protocols remove buildup with mild solvents.

| Practice | Frequency | Cost Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Monthly | Low | |
| Repair | As needed | $200 avg | |
| Cleaning | Weekly | Minimal |
Regular efforts prolong life, dodging surprise halts.
Selection Criteria for Black Rubber Belts
What’s the real story behind picks? Load assessment weighs max tonnage. Environmental fit considers temperature and moisture.

| Criteria | Assessment | Match Grade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load | Tonnage calc | High tensile | |
| Environment | Temp/humidity | Oil-resistant |
Smart choices tune performance to challenges.
Cost and Sourcing Considerations
Ready for the good part? Pricing factors include grade and length. Supplier evaluation focuses on certifications like ISO.

| Factor | Price Range | Lifespan Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | $10-50/m | 2-5 years | |
| Supplier | Certified | Quality assured |
Quality buys save via less downtime.
Black rubber conveyor belts shine in tough tasks, solving handling woes across sectors. Prioritize durability for efficiency gains—audit your systems now to boost output and cut costs. For more, check industry standards from ISO.
FAQ
Q1: What defines a black rubber conveyor belt? A: Durable rubber material designed for heavy loads, offering abrasion resistance and flexibility in industrial transport.
Q2: How long does a black rubber belt last? A: Typically 2-5 years under standard use, depending on load and maintenance practices.
Q3: Can it handle high temperatures? A: Yes, specialized grades resist up to 200°C for hot material applications.
Q4: What maintenance is required? A: Regular inspections for wear, cleaning, and tension adjustments every 3-6 months.
Q5: How to choose the right grade? A: Assess load weight, material type, and environment to match tensile strength needs.

