In high-stakes industries like mining and logistics, a single conveyor belt failure can bring operations to a sudden stop, creating costly downtime and draining productivity. Inconsistent or low-quality belts only worsen the problem, putting pressure on budgets and teams. Gaining a clear understanding of the rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process provides the insight needed to select or build belts engineered for superior strength, stability, and longevity. With decades of industrial expertise behind it, the rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process empowers businesses to maintain smoother production lines and achieve more reliable, efficient operations.
1. Overview of Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
This process shapes raw rubber into durable belts through key stages like mixing, calendaring, laminating, vulcanizing, and inspecting. Rubber stands out for its elasticity and toughness, ideal for handling heavy loads in tough spots. Industries gain from belts that cut maintenance and boost throughput, scaling easily for bulk ops.
What defines this process?
It starts with compounding rubber for strength.
Why focus on rubber materials?
They flex without cracking under stress.
How does it benefit industries?
Reliable belts mean fewer stops and higher yields.
Key Takeaway: Understanding the full process empowers you to select belts that minimize disruptions and maximize efficiency.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compounding | Blending rubber base | Enhances strength | |
| Key Stages | Mixing to inspecting | Ensures durability | |
| Industry Use | Heavy load handling | Reduces downtime |
Analyzing the overview highlights how integrated stages create resilient belts, guiding you to prioritize quality from the start.
2. Preparation in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Gather natural or synthetic rubber, fabrics, and additives like sulfur. Source from vetted suppliers to dodge impurities that weaken bonds. Preheat everything evenly, around 50-60°C, to blend smoothly later.
What raw materials are needed?
Polymers form the base, with steel cords for reinforcement.
How do you source quality rubber?
Test for tensile specs and trace origins.
Why preheat components?
It breaks down lumps for uniform mixes.
Key Takeaway: Proper preparation sets the foundation for a belt that withstands rigorous demands without early failures.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Rubber, fabrics, additives | Builds core structure | |
| Sourcing | Vetted suppliers, tests | Avoids impurities | |
| Preheating | 50-60°C even heat | Ensures smooth blending |
This stage’s focus on quality sourcing prevents costly defects, so audit your suppliers regularly for optimal results.
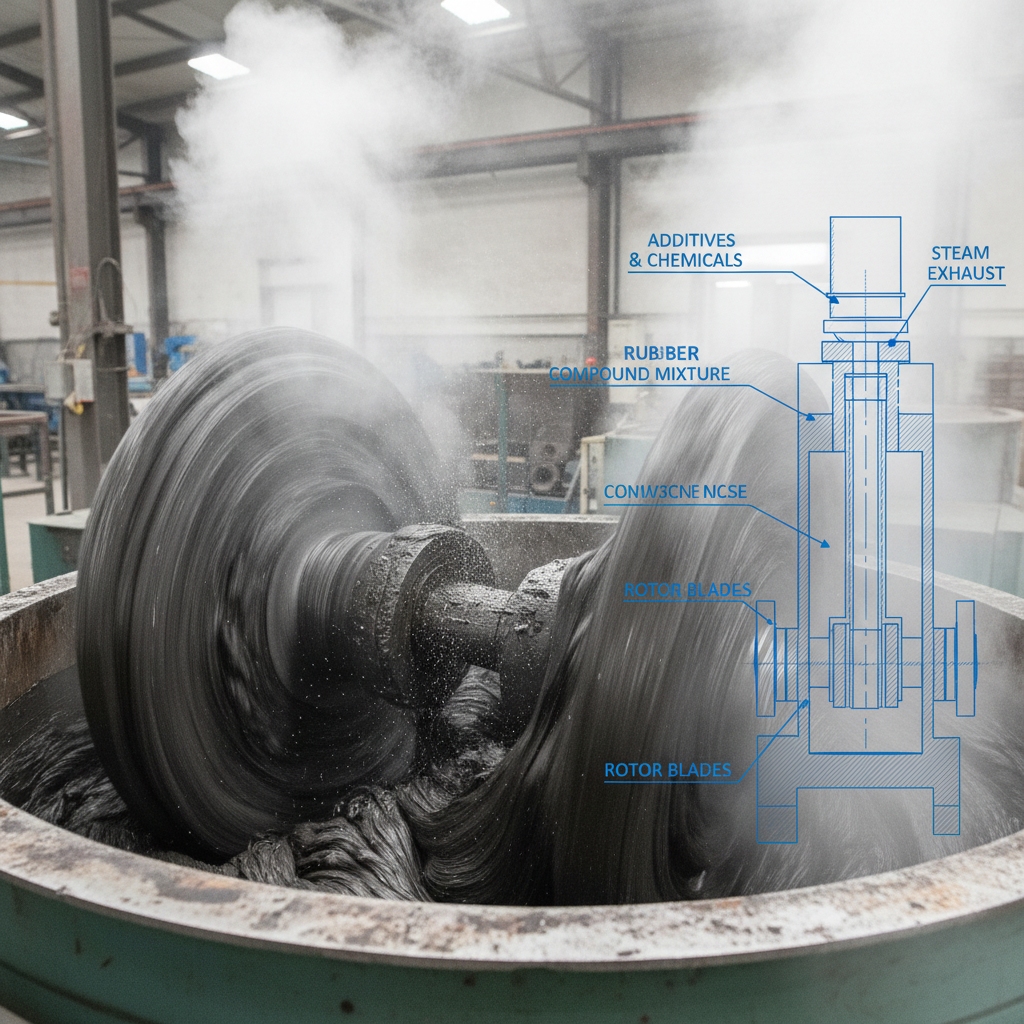
3. Mixing in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
In massive internal mixers, blend rubber with fillers and accelerators at high shear. This creates a uniform compound, tweaking the rubber’s chains for better wear resistance. Agents like carbon black boost durability.
What happens during compounding?
Ingredients fuse into a dough-like mass.
How do agents alter rubber structure?
They link molecules for elasticity.
Why use internal mixers?
They ensure no weak zones form.
Key Takeaway: Effective mixing transforms raw inputs into a resilient compound you can rely on for high-performance belts.
| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blending | High shear in mixers | Uniform compound | |
| Agents | Carbon black, accelerators | Improves wear resistance | |
| Structure | Molecular linking | Boosts elasticity |
Mastering mixing uniformity reduces wear, helping you extend belt life in demanding environments.
4. Calendaring in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Feed fabric through heated rollers to coat it thinly with rubber. Skim extra layers on cords for grip. Keep temps at 80-100°C to prevent air pockets.
How is fabric coated?
Rollers squeeze and spread evenly.
What role does skimming play?
It seals fibers tightly.
Why control coating temperature?
It avoids bubbles that compromise strength.
Key Takeaway: Calendaring ensures a seamless coating that protects your conveyor from environmental stresses.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating | Heated rollers on fabric | Even thin layer | |
| Skimming | Extra on cords | Enhances grip | |
| Temperature | 80-100°C control | Prevents air pockets |
Precise temperature in calendaring safeguards belt integrity, so calibrate equipment to avoid structural weaknesses.
5. Cover Sheeting in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Roll the mix into flat sheets, 2-5mm thick, for top and bottom covers. Inspect for smoothness to fend off abrasions. Apply both sides for full protection.
How do you form rubber films?
Precision mills flatten precisely.
What ensures surface quality?
Gauges check thickness.
Why apply to top and bottom?
It shields from dirt and impacts.
Key Takeaway: Dual-sided sheeting provides comprehensive protection, keeping your operations abrasion-free.
| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forming | Mills for 2-5mm sheets | Flat covers | |
| Inspection | Gauges for smoothness | Prevents abrasions | |
| Application | Top and bottom sides | Full shielding |
Quality sheeting inspection minimizes exposure risks, enabling longer service in harsh conditions.
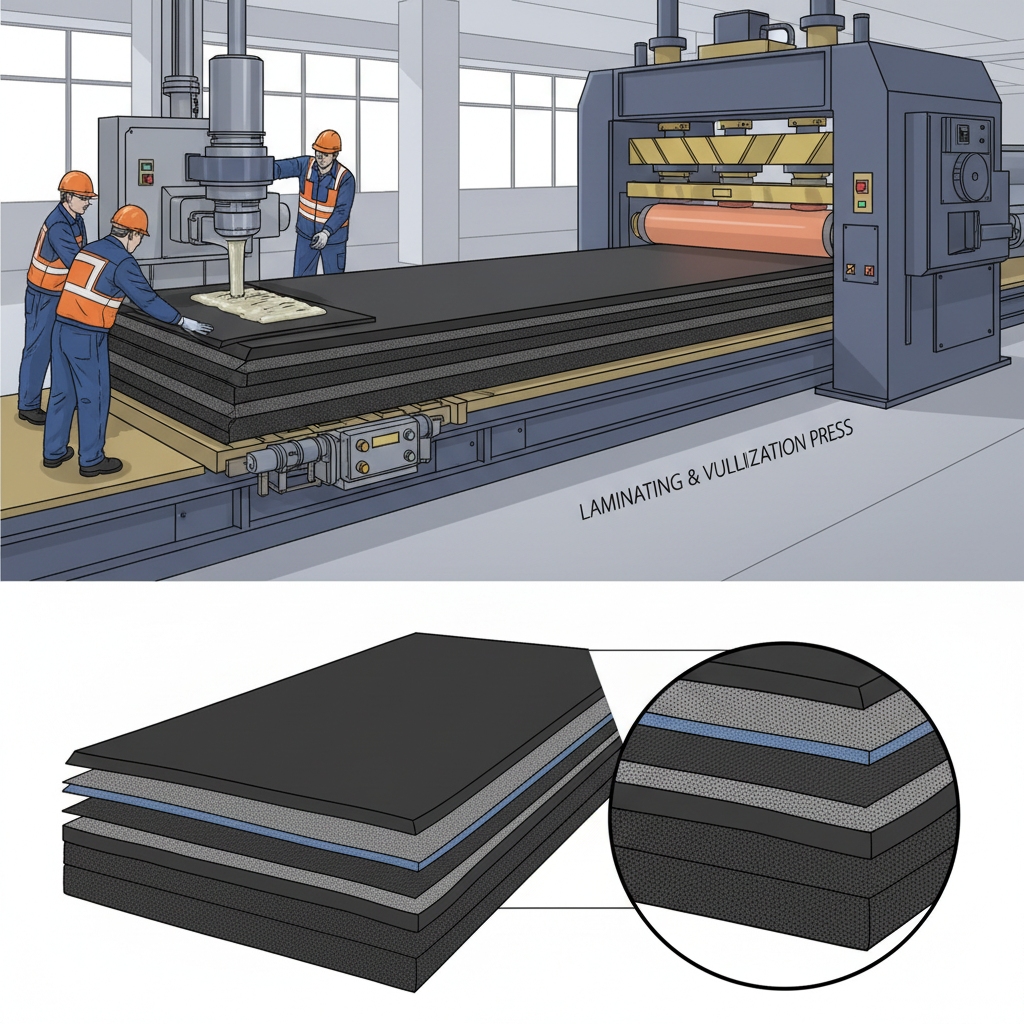
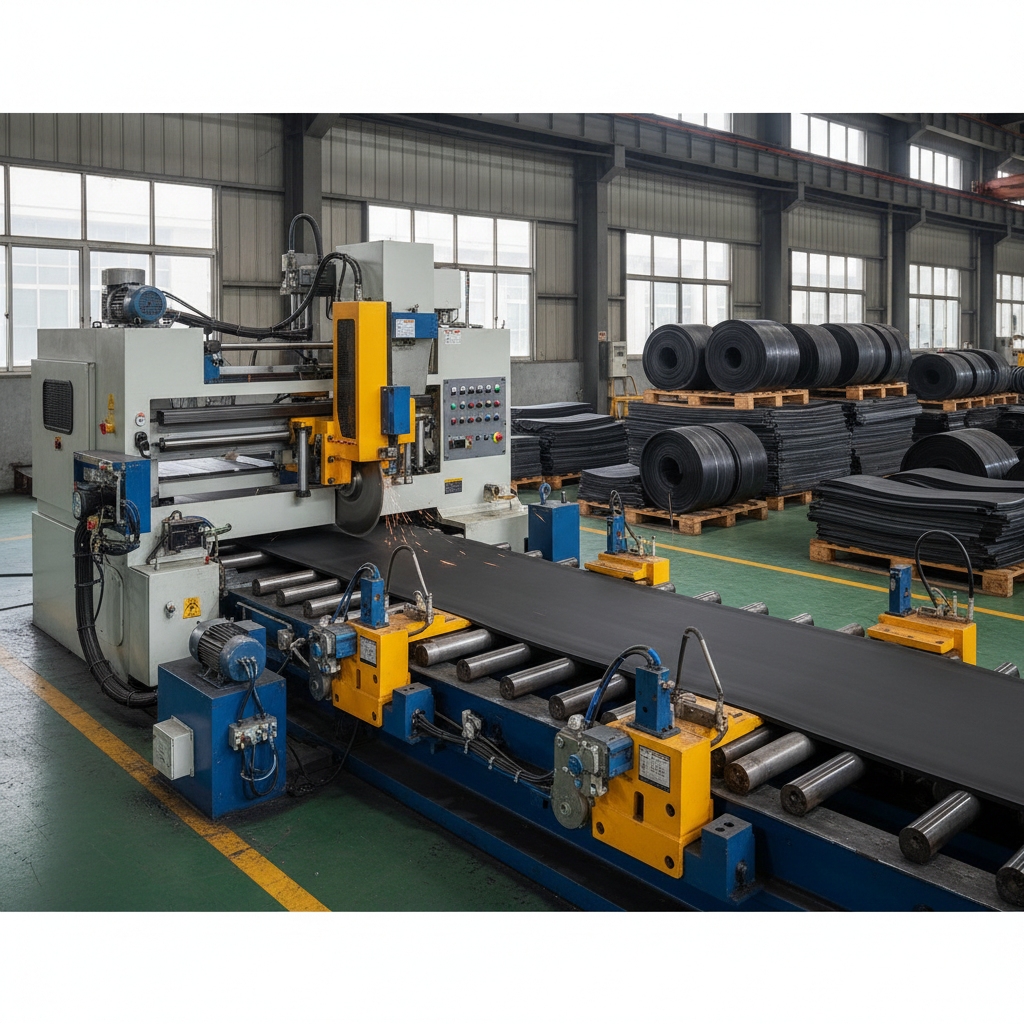
6. Laminating in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Stack the core fabric, covers, and edge strips under steady tension. Align layers lengthwise to form the belt body. This builds a solid, warp-free structure.
What layers are assembled?
Carcass in the middle, covers out.
How maintain tension uniformly?
Drums guide without pulls.
Why add edge rubber?
It prevents fraying at sides.
Key Takeaway: Laminating creates a unified belt structure that resists warping under load.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stacking | Core, covers, edges | Solid body | |
| Tension | Drum guidance | Warp-free alignment | |
| Edges | Rubber strips | Anti-fraying |
Uniform tension in laminating ensures stability, so monitor alignment to prevent operational twists.
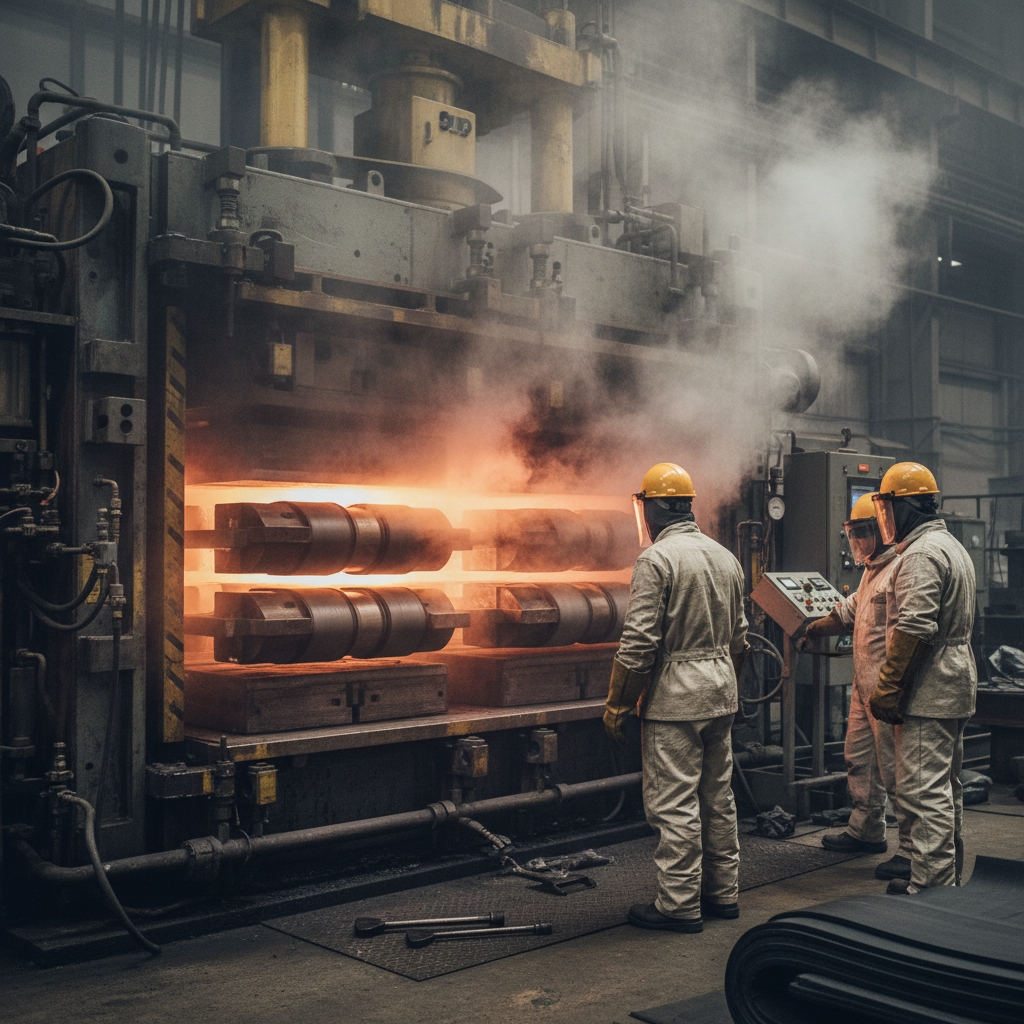
7. Vulcanizing in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Press the assembly in molds at 150°C with steam, triggering sulfur cross-links. This hardens rubber into a resilient network. It’s the make-or-break for longevity.
What chemical reaction occurs?
Bonds form between chains.
How does heat cross-link polymers?
Pressure speeds the cure.
Why is this step critical?
It locks in flexibility and toughness.
Key Takeaway: Vulcanizing finalizes the belt’s resilience, making it ready for tough industrial use.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressing | 150°C steam in molds | Cross-links sulfur | |
| Reaction | Chain bonding | Hardens network | |
| Criticality | Locks properties | Ensures longevity |
Vulcanizing’s cross-linking defines durability, so precise timing prevents over- or under-curing issues.
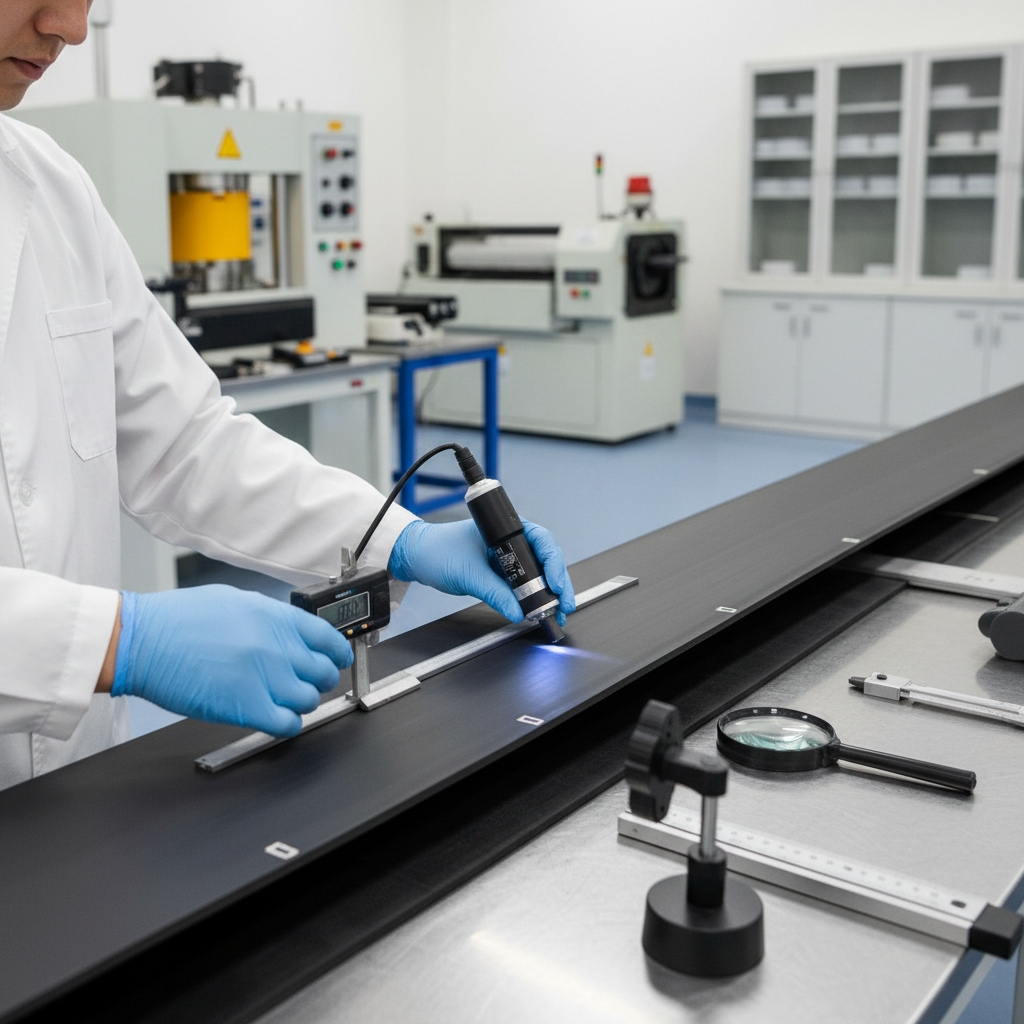
8. Inspecting in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Measure lengths, test pulls up to 15% elongation, and scan for cracks. Visual checks catch surface flaws early. Compliance ensures safe use.
What size tests are performed?
Calipers verify widths.
How check physical properties?
Machines simulate loads.
Why examine appearance?
Flaws signal failures ahead.
Key Takeaway: Thorough inspection guarantees belts meet safety standards, protecting your team and assets.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Lengths, widths with calipers | Accurate sizing | |
| Pull Tests | Up to 15% elongation | Simulates loads | |
| Visual Scans | Crack detection | Early flaw catch |
Rigorous inspection uncovers hidden defects, helping you deploy only reliable belts in production.
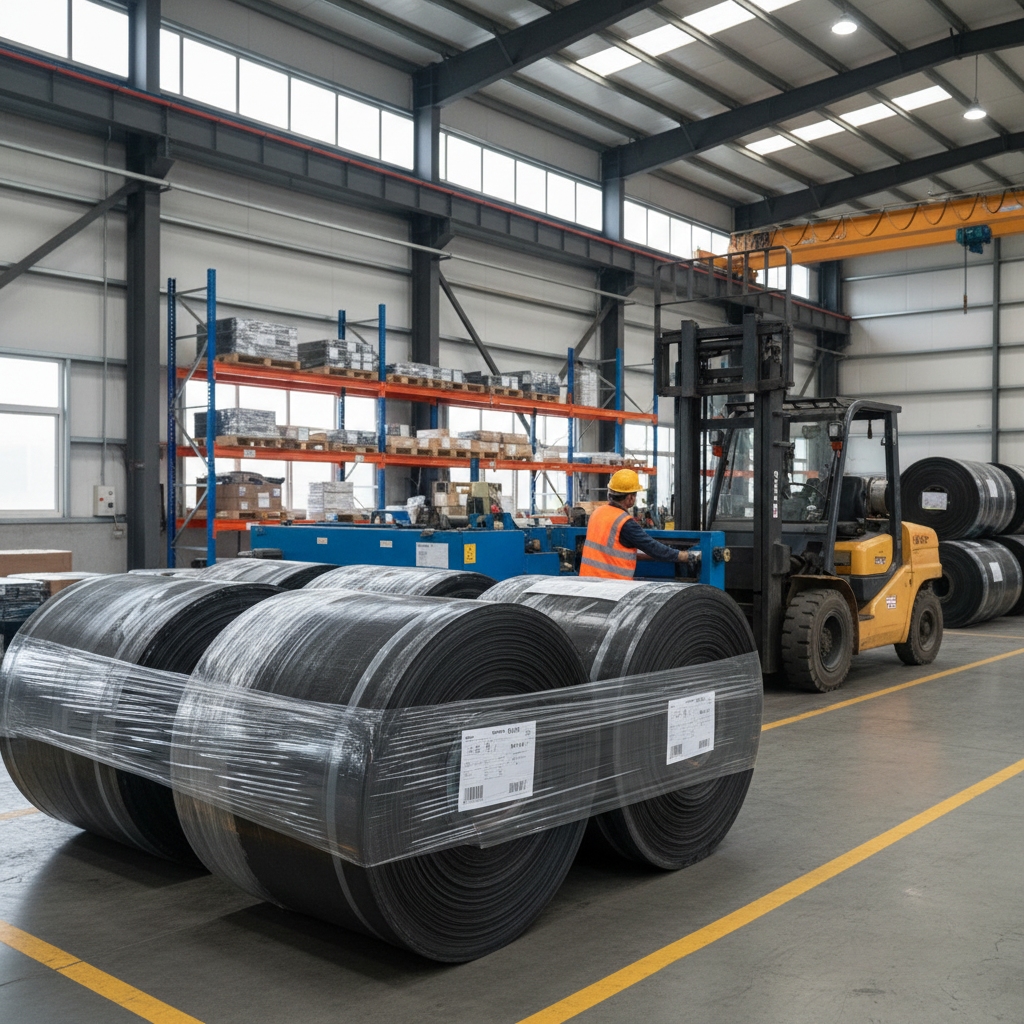
9. Packing in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Coil belts loosely, wrap in plastic, and crate them. Use anti-moisture barriers. Labels note specs for easy tracking.
How protect belts during shipping?
Padding avoids bends.
What packaging materials work best?
Corrugated with desiccants.
Why label for traceability?
It speeds installs in warehouses.
Key Takeaway: Secure packing preserves belt quality from factory to your site.

| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coiling | Loose rolls | Prevents damage | |
| Wrapping | Plastic, desiccants | Moisture barrier | |
| Labeling | Spec details | Easy tracking |
Effective packing maintains integrity during transit, ensuring belts arrive ready for immediate use.
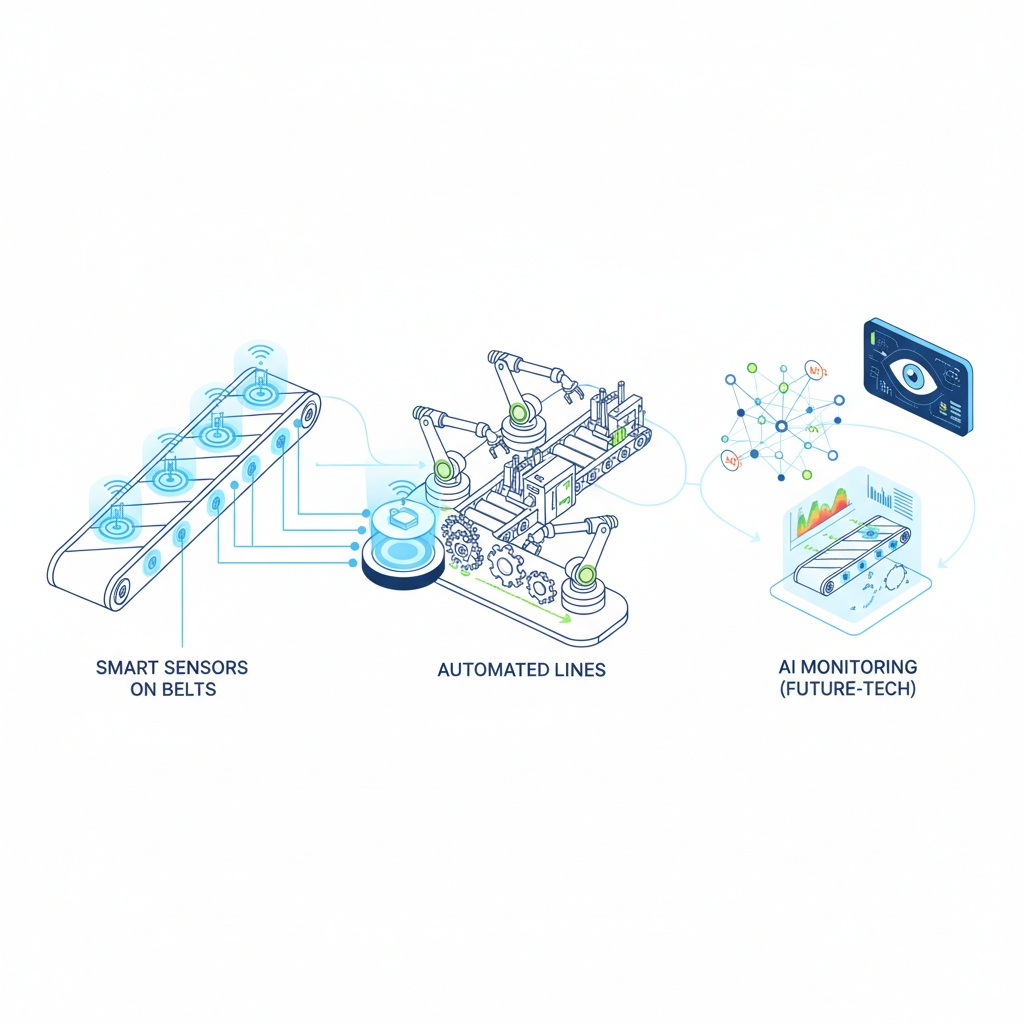
10. Innovations in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing Process
Eco-additives like bio-fillers cut waste. Robots handle mixing for speed. Sensors flag defects in real-time.
What eco-friendly additives emerge?
Recycled polymers shine.
How automate for efficiency?
PLCs streamline flows.
Why integrate smart monitoring?
It predicts breakdowns, saving costs.
Key Takeaway: Innovations like automation future-proof your conveyor systems for sustainability and efficiency.
| Aspect | Description | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Additives | Bio-fillers, recycled | Reduces waste | |
| Automation | Robots, PLCs | Speeds processes | |
| Monitoring | Real-time sensors | Predicts issues |
Adopting innovations in monitoring cuts predictive maintenance costs, positioning you ahead in efficient manufacturing.
In wrapping up, unreliable belts drain your bottom line, but diving into the rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process—from prep to packing—unlocks durable gear that powers your ops. Picture seamless runs ahead. Audit your setup now and reach out to pros for tweaks that amp efficiency.
FAQ
Can I customize rubber compounds? Yes, tailor for heat or oil resistance to fit your setup, extending belt life.
Can I skip temperature controls in calendaring? No, it risks weak bonds and early failures under stress.
Can vulcanizing times vary by belt type? Sure, adjust for thickness—thinner needs less time for even curing.
Can I use recycled materials in mixing? Absolutely, if tested, it trims costs while keeping quality solid.
Can inspection be automated fully? Partly, with cameras, but experts add the final eye for precision.

