Struggling with conveyor belts that wear out too quickly, interrupting your B2B operations and driving up maintenance costs? The solution starts with understanding the rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process. By exploring how mixing, calendering, reinforcement layering, and vulcanization work together, you gain insight into what makes a belt truly durable and capable of withstanding heavy industrial demands. With decades of experience optimizing material-handling systems, this guide breaks down the rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process so you can choose reliable, long-lasting solutions that minimize downtime and keep production running smoothly.
Table of Contents
1. What Materials Are Selected in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?

Selecting materials forms the backbone of rubber conveyor belt manufacturing. Key raw components include natural rubber for elasticity or synthetic types like neoprene for chemical resistance. You might be wondering: Why choose one over another? Natural versions flex well under loads, yet synthetics endure harsh environments better. Reinforcements such as nylon fabrics or steel cords add tensile strength, preventing tears during transport. This choice directly impacts belt lifespan in factories. For instance, mining firms opt for abrasion-resistant synthetics to haul ores without quick degradation. Proper picks avoid early failures, saving replacement expenses. Blending these ensures uniformity across production runs.
| Material | Benefit | Drawback | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Elasticity | Poor heat tolerance | |
| Synthetic Rubber | Durability | Costlier | |
| Steel Cords | High strength | Increases weight |
2. How Does Mixing Occur in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?

Mixing blends rubber compounds uniformly, a critical phase in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing. Machines combine base rubber with additives like carbon black for reinforcement or antioxidants to fight aging. But here’s the kicker: Factors like temperature and shear force guarantee consistency, avoiding lumps that weaken final products. Additives enhance properties—silica improves grip, while oils soften mixes for easier processing. In practice, automotive plants rely on precise blends to create belts handling oily parts without slippage. This step sets quality foundations, influencing everything from flexibility to load capacity. Poor mixing leads to uneven wear, hiking maintenance needs in B2B settings.
3. What Happens During Extrusion in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?

Extrusion shapes rubber into continuous sheets during rubber conveyor belt manufacturing. Heated material passes through dies, controlled by temperature around 80-100°C for smooth flow. Ready for the good part? Precision tools maintain thickness, preventing thin spots that cause breaks. Speed at 10-20 meters per minute ensures even output, vital for custom widths in assembly lines. Food processing uses this to form hygienic covers resisting bacteria. Variations adjust for cleated or flat designs, optimizing material movement. Effective extrusion cuts waste, boosting efficiency for manufacturers supplying logistics firms.
| Parameter | Range | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 80-100°C | Flow control | |
| Speed | 10-20 m/min | Evenness | |
| Pressure | 50-100 bar | Density |
4. Why Layer and Assemble in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?
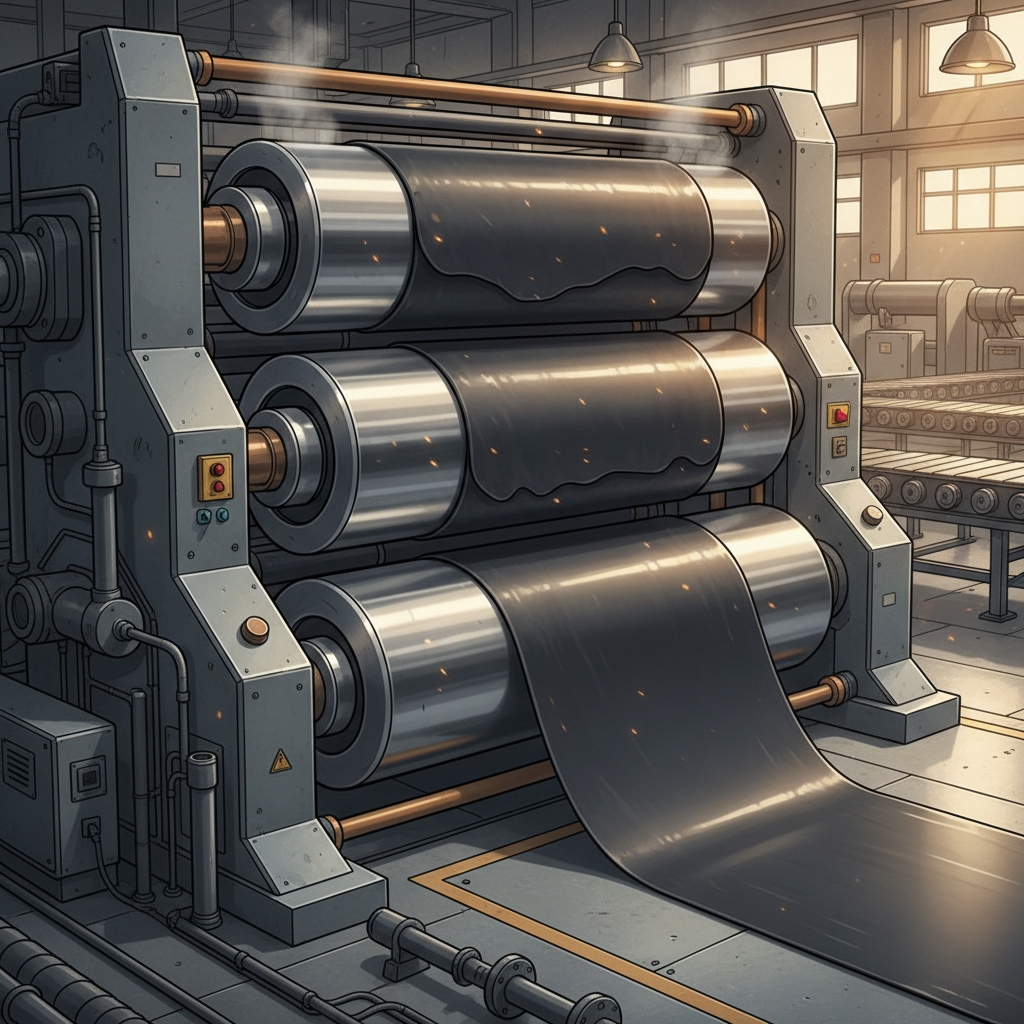
Layering builds multi-ply structures in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing, integrating covers, cushions, and reinforcements. Calendaring presses fabrics into rubber for smooth bonds. What’s the real story? Effective integration distributes stress evenly, extending service under vibrations. Steel cords in cores handle 100-ton pulls in ports, while nylon suits lighter duties. Assembly lines align layers precisely, avoiding delamination risks. Chemical plants benefit from this for belts carrying corrosives without separation. Techniques like drum wrapping ensure adhesion, reducing operational halts.
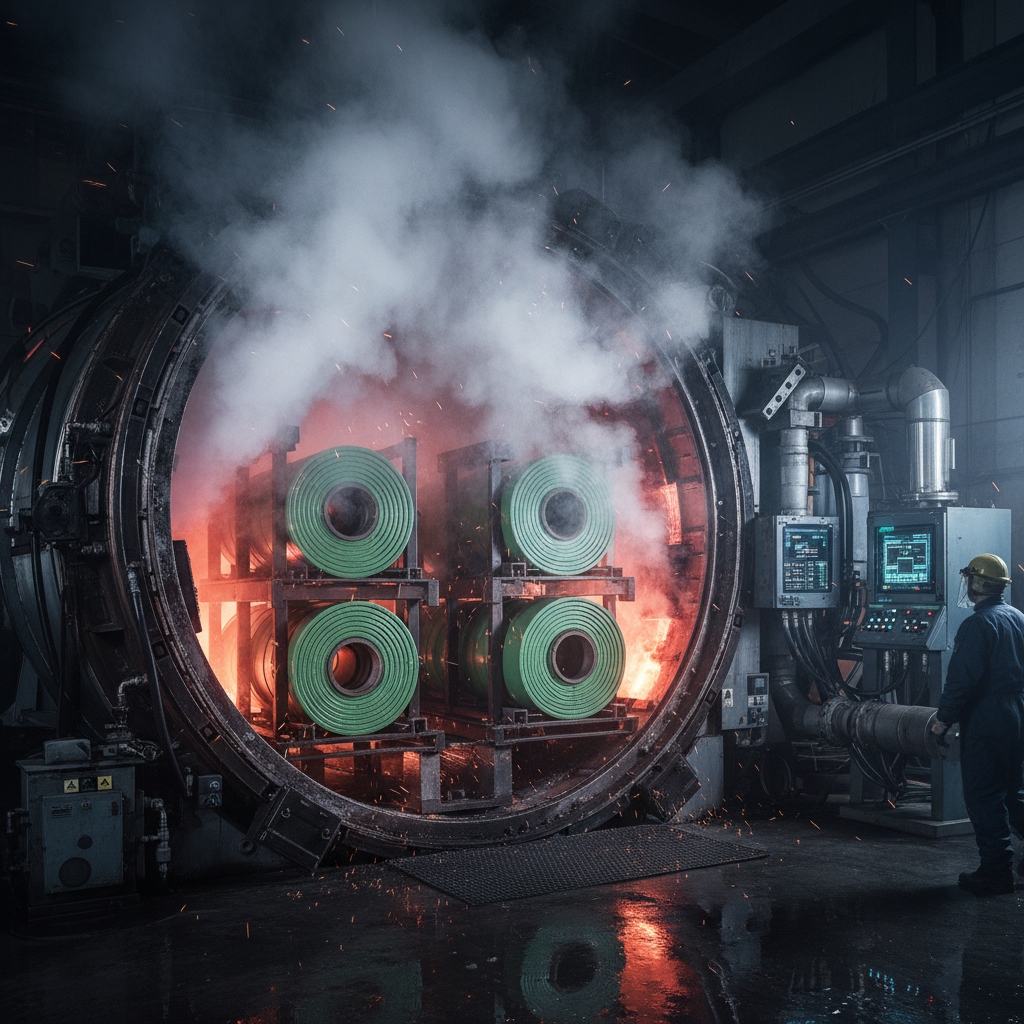
5. What’s the Vulcanization Step in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?

Vulcanization cures rubber using heat, pressure, and sulfur in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing. At 150-180°C, it cross-links molecules, boosting strength. This is where it gets interesting: Without it, belts remain soft and prone to stretching. Variations suit types—autoclaves for thick ones, hot air for thinner. Oil rigs use vulcanized belts enduring submersion. This transforms pliable sheets into resilient products, vital for safety in warehouses.
| Method | Temperature | Duration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autoclave | 150-180°C | 20-40 min | |
| Hot Air | 140-160°C | 30-60 min |
6. How Is Cooling Done in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?
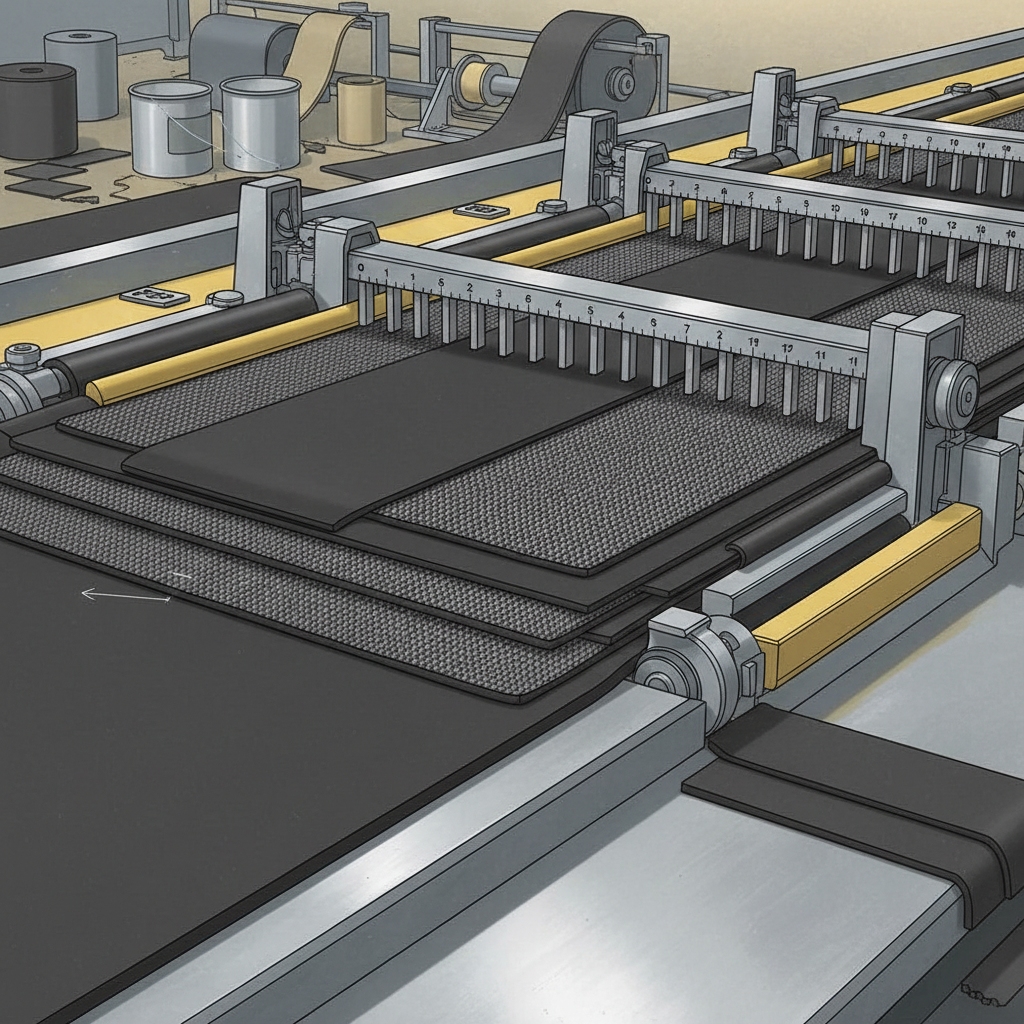
Cooling solidifies vulcanized belts in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing, preventing warping. Air or water methods lock properties rapidly. Now, picture this: Slow cooling causes cracks; quick versions maintain integrity. Racks hold belts for 10-60 minutes, ensuring flatness for splicing. Textile mills apply controlled chambers for uniform results, fitting machinery perfectly. This step finalizes shapes, minimizing defects in high-volume production.
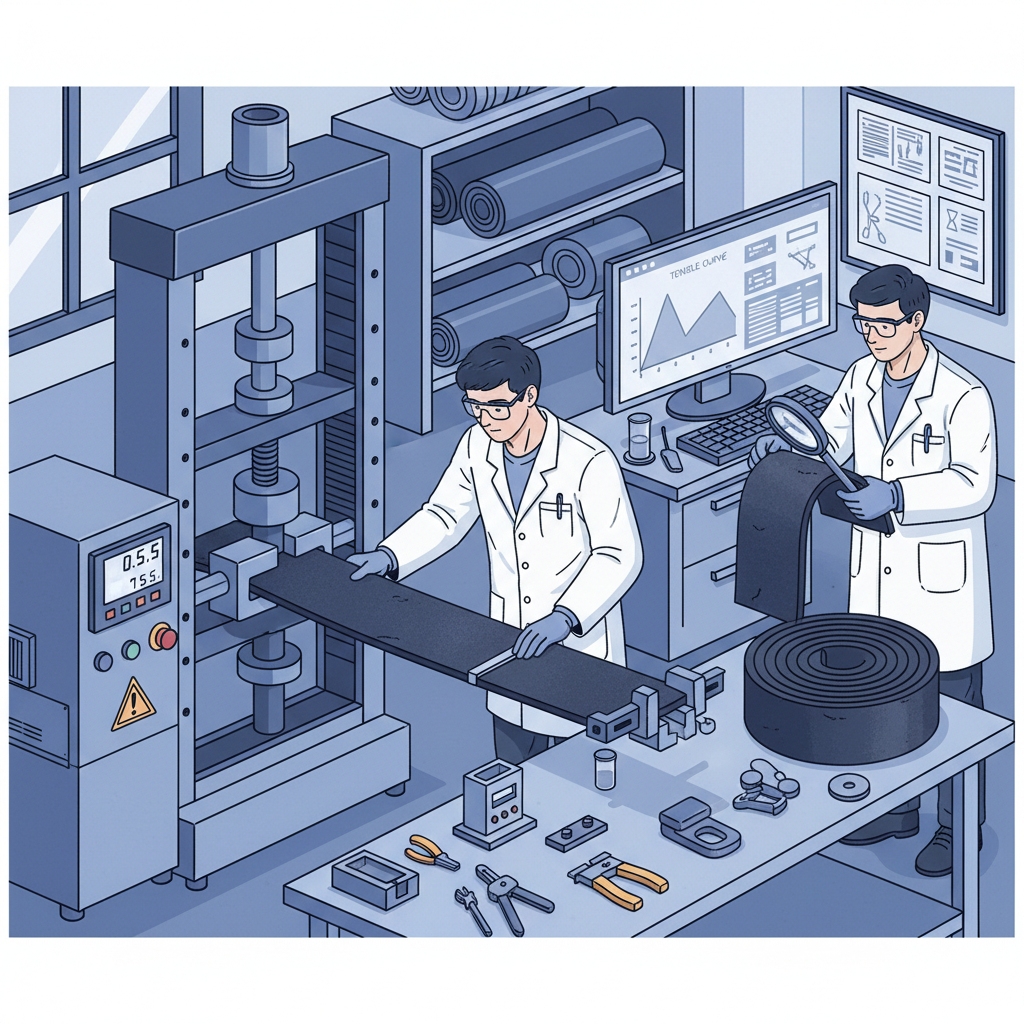
7. What Quality Checks Follow in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?

Quality tests verify standards in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing, including tensile pulls and abrasion simulations. Can early detection save costs? Yes—X-rays spot internal flaws before shipment. Labs measure elongation under 10% load for reliability. Steelworks demand these to avoid breakdowns hauling metals. Routine checks cut returns, enhancing B2B trust.
| Test | Metric | Standard | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile | >15 MPa | Strength | |
| Abrasion | <150 mm³ | Wear resistance |
8. Can You Customize in Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?
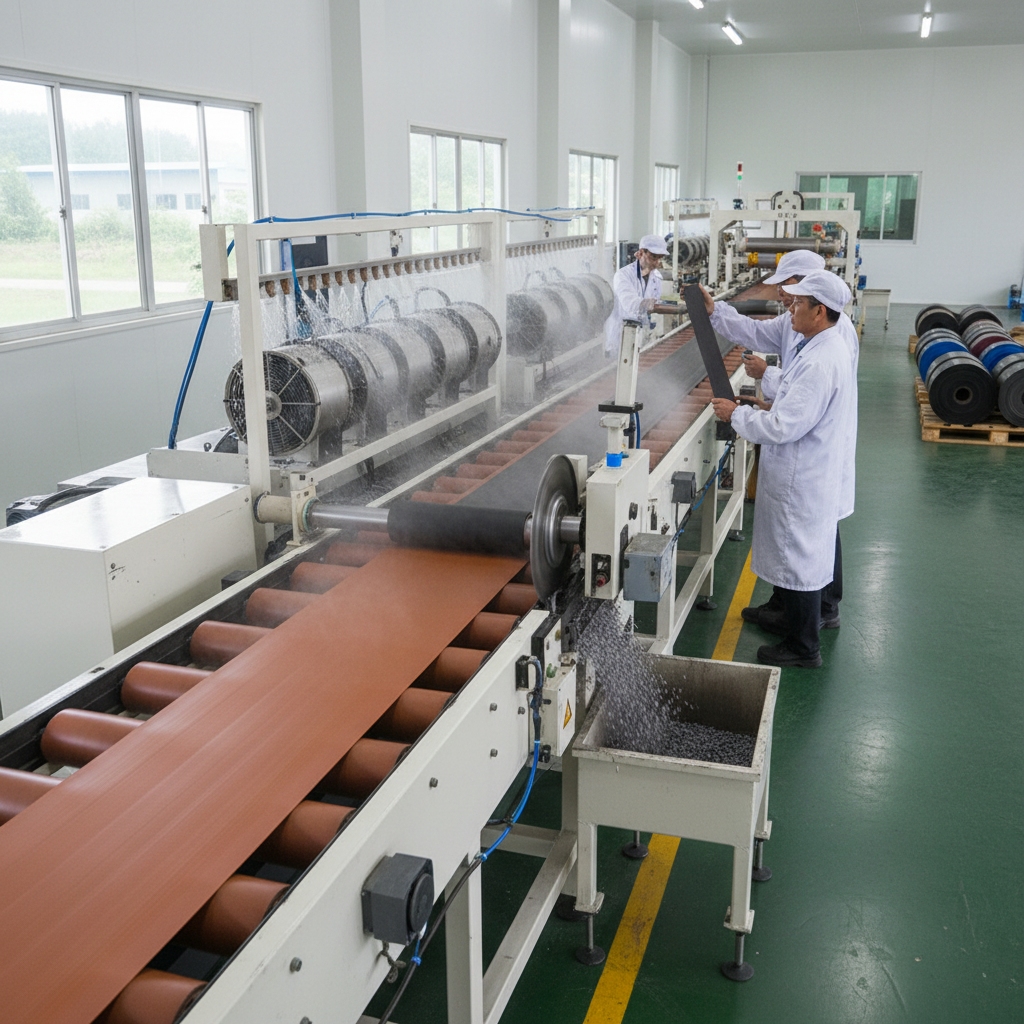

Customization tailors belts in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing to specific needs, like adding cleats for inclines. You might wonder: Features like anti-static layers boost safety in electronics. Design focuses on longevity through thicker covers. Breweries customize for wet environments, preventing slips.
9. Where Are Rubber Conveyor Belts Applied?

Applications span industries in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing outputs. Mining uses abrasion-proof versions for ores. Here’s how it works: Process enables versatility, from agriculture’s flexible belts to logistics’ speedy ones. Ports handle containers efficiently, cutting labor.
| Industry | Use | Feature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining | Ore haul | Toughness | |
| Agriculture | Crop move | Bendability |
10. How Does Sustainability Fit Rubber Conveyor Belt Manufacturing?

Sustainability incorporates recycled rubbers in rubber conveyor belt manufacturing, reducing waste. Why recycle? It maintains performance while lowering emissions. Trends favor bio-based additives for eco-compliance. Manufacturers adopt closed loops, appealing to green B2B clients.
In summary, grasping the rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process empowers better choices, slashing downtime and costs. Prioritize quality materials and checks for peak performance. Ready to upgrade? Consult experts for tailored advice—your operations deserve reliability.
FAQ
Q1: What materials work best for heavy loads? Steel-reinforced synthetics excel, offering superior strength without excessive flex, ideal for mining transport.
Q2: How does vulcanization improve belts? It creates durable bonds, resisting tears and heat far better than uncured rubber.
Q3: Can belts use recycled content? Yes, recycled materials integrate seamlessly, preserving quality while supporting eco-goals.
Q4: What’s key to extrusion success? Temperature and speed control ensure uniform sheets, avoiding weak areas.
Q5: How often test manufactured belts? Every six months via tensile and wear exams prevents unexpected failures.

