Pipe Conveyor Belt — Fully Enclosed, Clean & Efficient Bulk Handling
Pipe Conveyor Belt: Revolutionary Enclosed Transport System
Transform your material handling with our advanced pipe conveyor belt technology, delivering superior performance through innovative tubular design that ensures efficient, clean, and versatile conveying solutions.
Fully Enclosed Material Transport
Our pipe conveyor belt encapsulates materials within a tubular structure, preventing spillage, dust emission, and contamination during transport. This enclosed design ensures pollution-free operation, protecting both your materials and the environment while maintaining workplace cleanliness and safety standards.
Steep Angle Conveying Capability
The tubular structure increases friction between materials and the belt's inner surface, enabling transport angles typically up to 30° or more. This steep-angle capability significantly reduces space requirements, allows for more compact system layouts, and decreases overall installation costs compared to conventional flat belt systems.
Flexible Spatial Layout Design
The pipe belt's tubular structure enables both vertical and horizontal curves, allowing the system to navigate around obstacles, cross roads, railways, and rivers without intermediate transfer points. This flexibility results in highly economical overall layouts with smaller curve radii, reducing land requirements and infrastructure costs.
Bidirectional Material Transport
Under specific process conditions, the pipe belt's return branch can also transport materials. With high-tensile steel cord core construction and optimized formulation design for process control, we produce high-strength, long-distance, large-diameter steel cord pipe conveyor belts capable of bidirectional operation for maximum operational efficiency.
Ready to revolutionize your material handling system?
Advanced Cover Rubber Formulation Technology
Our proprietary cover rubber formula delivers exceptional durability and performance through rigorous testing and optimization, ensuring your pipe conveyor belt withstands the most demanding operational conditions.
Superior Performance Specifications
- Excellent physical and mechanical properties combined with outstanding ozone and weather resistance
- Ozone resistance: 40°C, 50pphm, 96 hours - no static cracking
- Dynamic ozone resistance for harsh environments: 20% elongation, 15 cycles/min - no surface cracking after testing
- Comprehensive laboratory testing ensures reliability and longevity in real-world applications

⚠️ Critical Performance Difference
Pipe conveyor belts without proper ozone resistance develop aging cracks on the surface, leading to premature failure and costly downtime. Our advanced formula prevents these issues, ensuring extended service life and reduced maintenance costs.

Protect your investment with superior rubber technology
Request Technical Data SheetIndustry-Leading Low Rolling Resistance Performance
Backed by research from Hannover University and verified through rigorous testing, our pipe conveyor belts achieve significantly lower rolling resistance, reducing energy consumption and operational costs by up to 40% compared to standard products.
Scientific Research Foundation
According to Hannover University research, indentation rolling resistance accounts for 61% of the total resistance during belt transport operation. The indentation rolling resistance of the belt cover rubber and roller interaction represents the primary resistance factor in conveyor belt transportation.
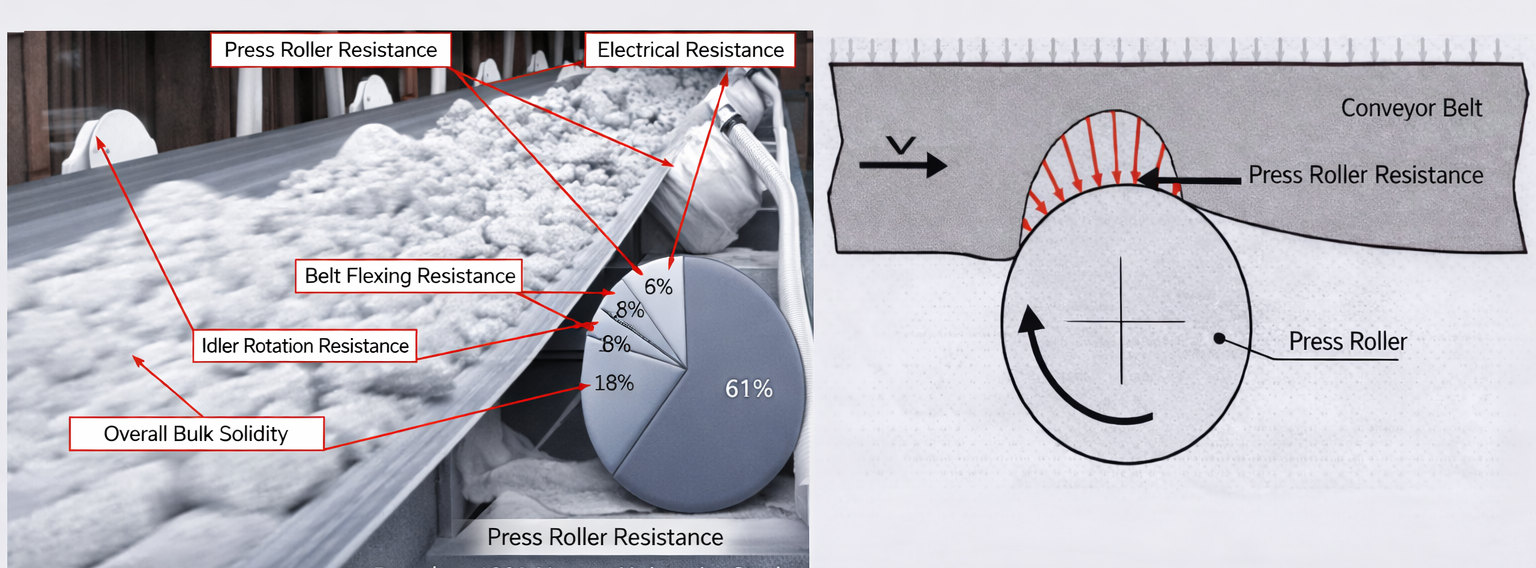
Industry Standard Requirement
≤ 0.1
The Rolling Resistance Factor (RRF) for the non-working surface cover layer of pipe belts must not exceed 0.1 according to industry standards.
Our Test Results
0.0465
Our steel cord pipe conveyor belt achieved RRF of 0.046459381, well below the standard requirement, demonstrating superior energy efficiency.
Energy Savings
53%
Lower rolling resistance translates to over 50% reduction in indentation resistance energy loss, significantly cutting operational electricity costs.
Test Frequency
GB/T 9870.2 StandardTesting frequency
Test Elongation
GB/T 9870.2 StandardElongation rate
Test Temperature
GB/T 9870.2 StandardTesting conditions
Experience the energy-saving advantages of our low rolling resistance technology
Download Test ReportsHigh-Performance Steel Cord Adhesion Technology
Our advanced core rubber formulation ensures exceptional bonding strength between steel cords and rubber, delivering superior fatigue resistance and extended service life for demanding continuous operations.
Superior Adhesion Performance
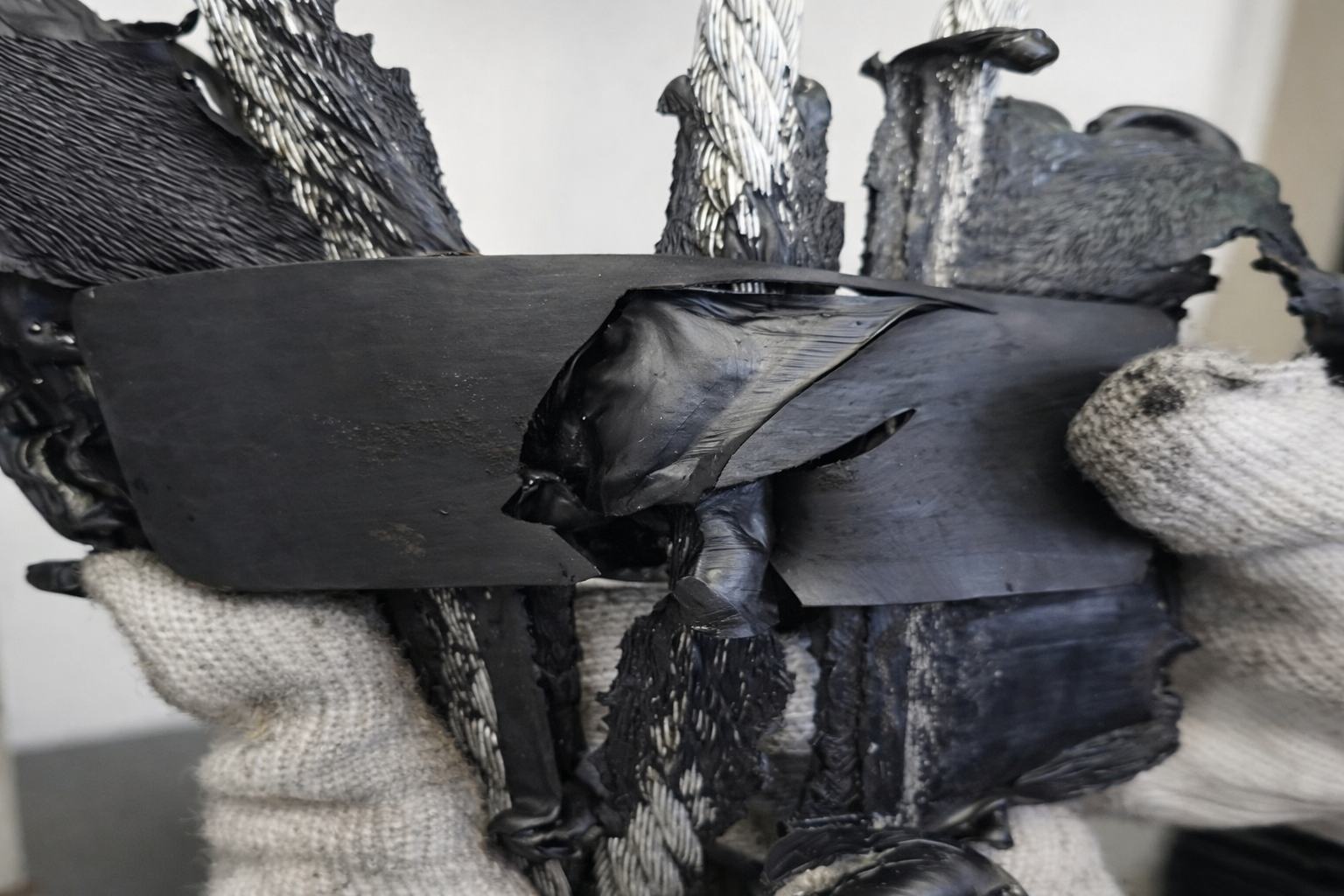
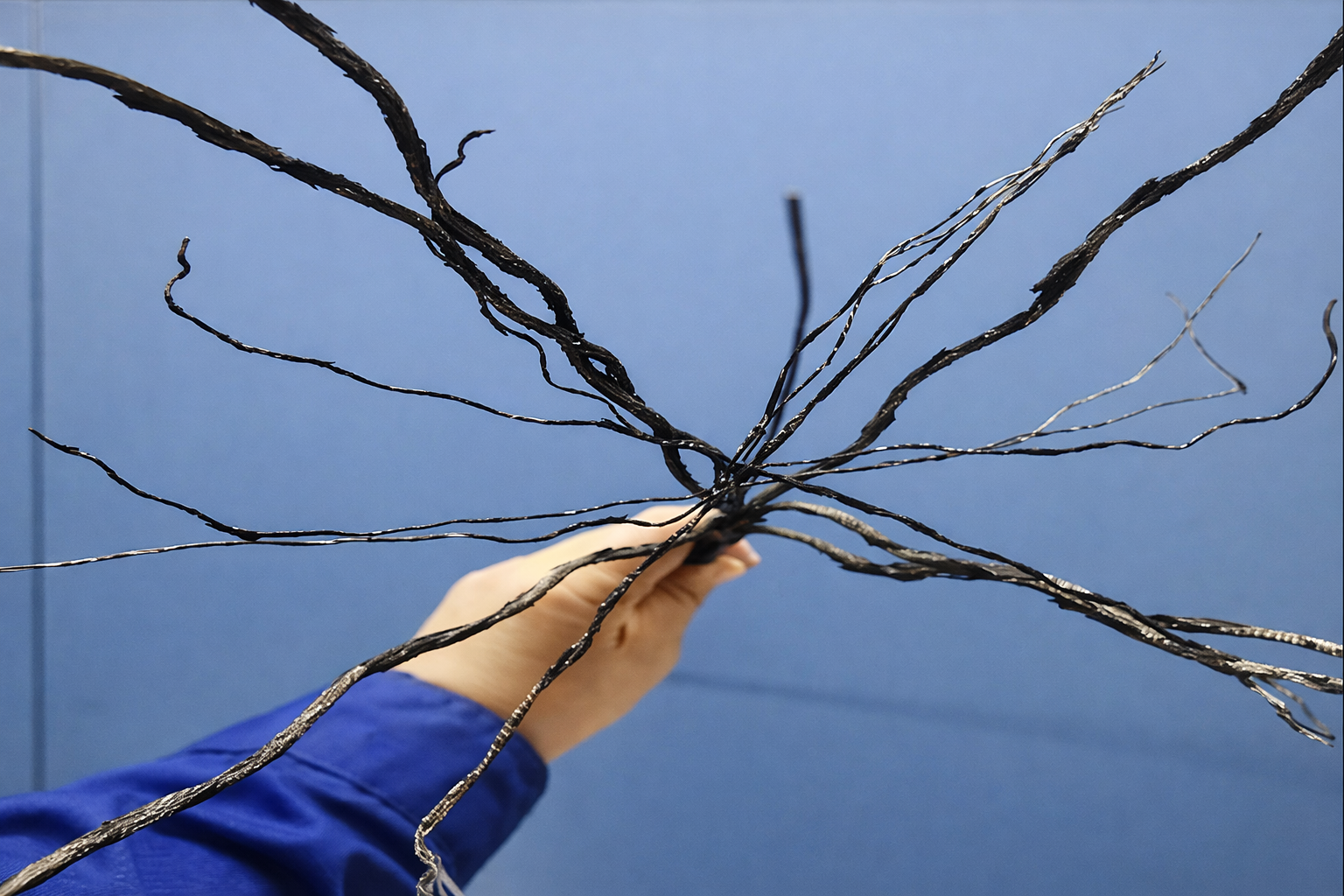


Ensure maximum reliability with our proven steel cord adhesion technology
View Adhesion Test DataComprehensive Structural Testing & Verification
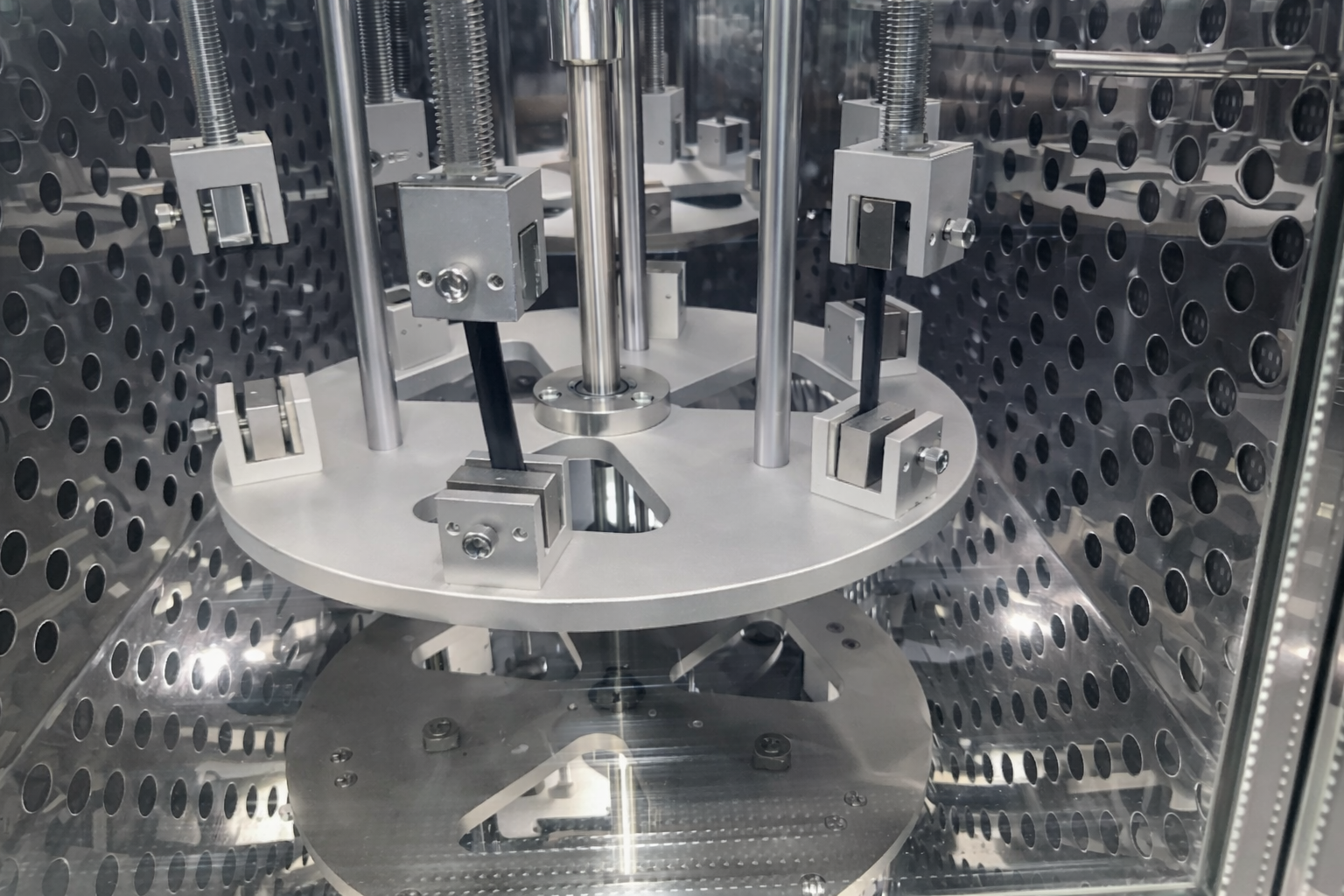
Our rigorous multi-phase testing program validates pipe formation capability, rigidity characteristics, and fatigue resistance, ensuring optimal performance in real-world operating conditions.
Optimized Structural Design Development
We develop and manufacture samples with different process structures based on engineering requirements, conducting comparative testing to validate and select the most suitable structural configuration for each application.
This systematic approach ensures optimal balance between flexibility for pipe formation, structural rigidity for load bearing, and long-term durability under continuous operation.
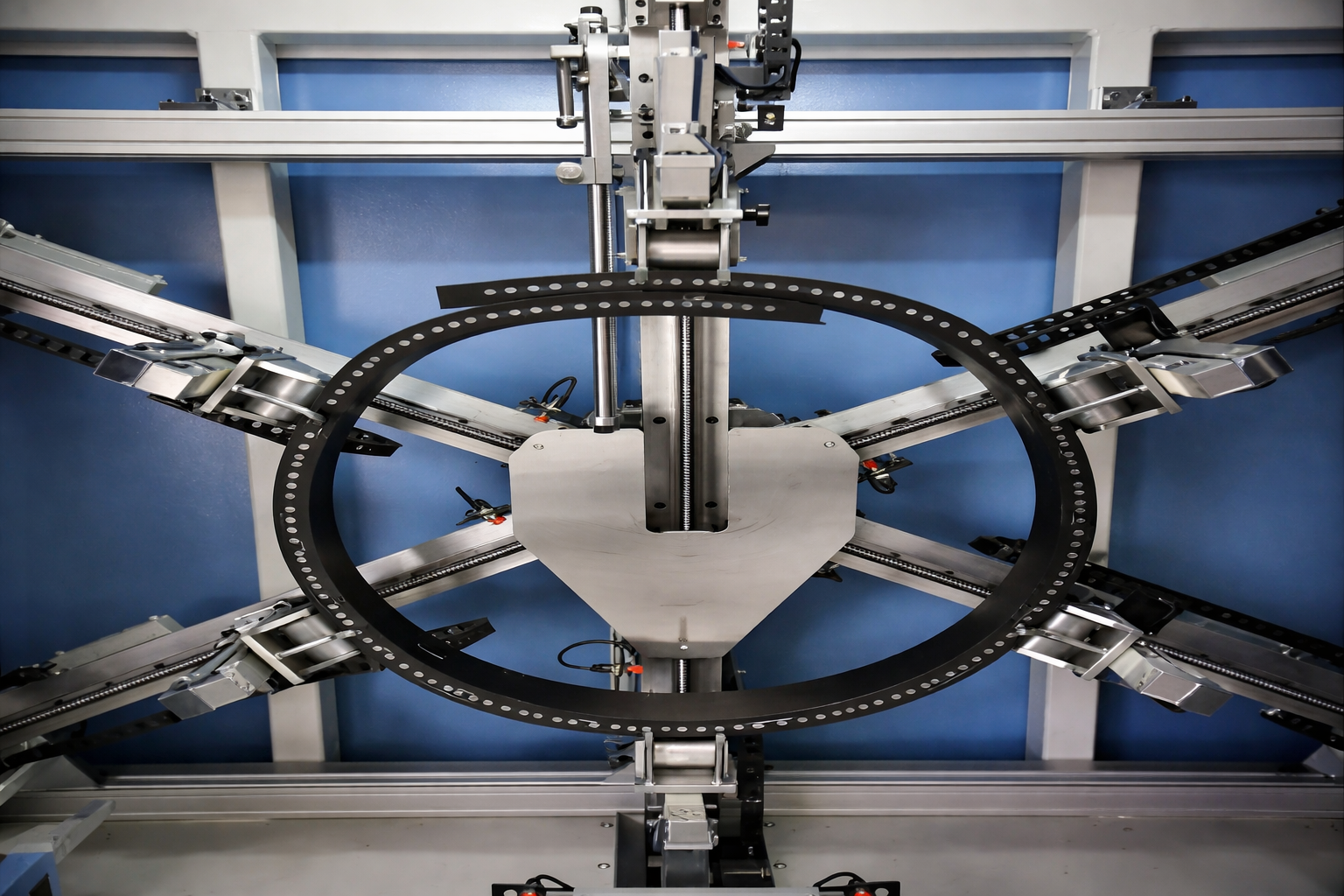

Pipe Formation & Rigidity Testing
Advanced testing equipment evaluates the belt's ability to form and maintain tubular shape under various tension conditions. Our rigidity testing ensures proper balance between flexibility for forming and stiffness for structural integrity during operation.
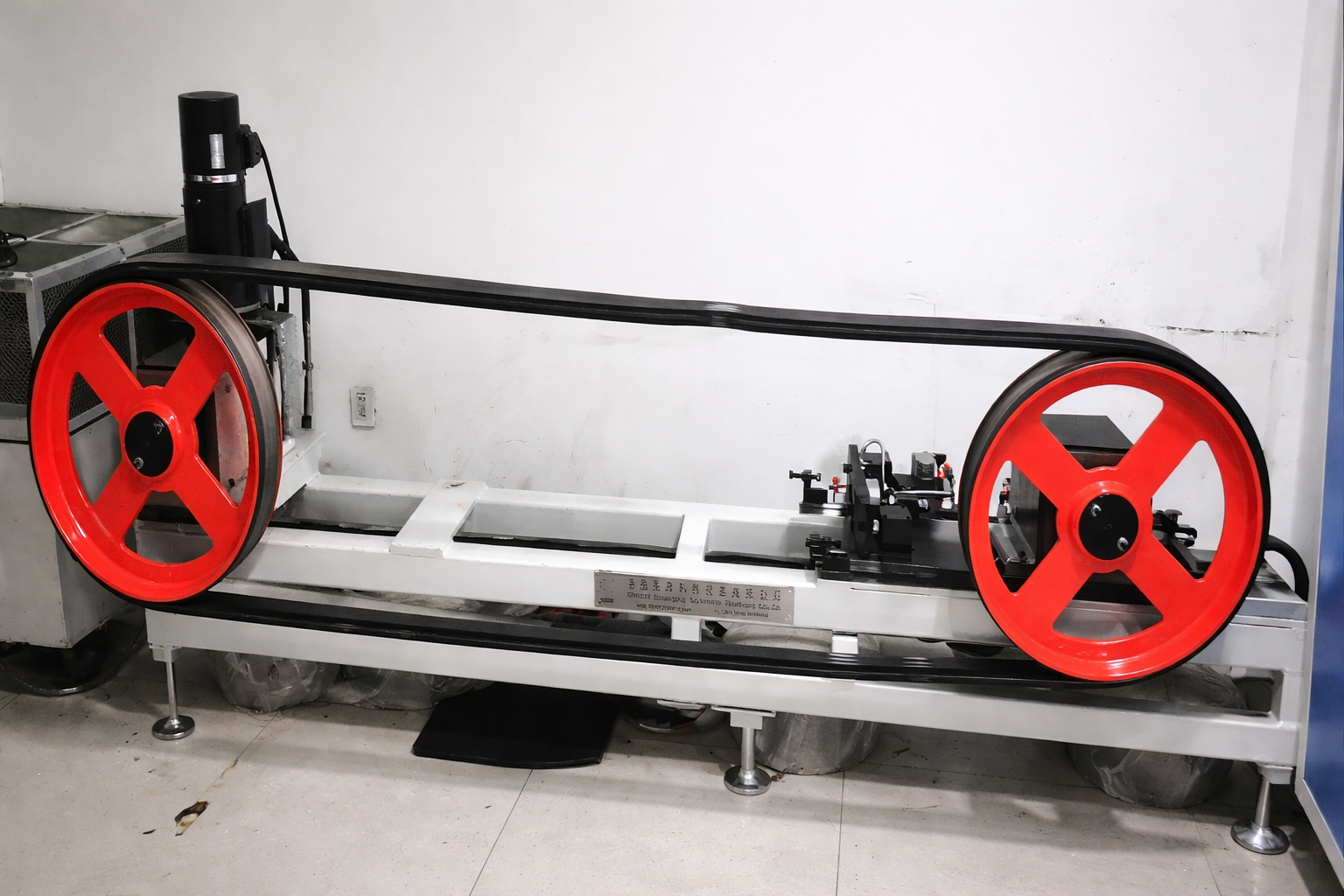
Dynamic Fatigue Verification
Continuous cycling tests simulate years of operational stress, validating long-term performance and identifying potential failure modes before production. This comprehensive testing guarantees reliability throughout the belt's service life.
Confidence through proven performance validation
Request Testing ProtocolsCritical Performance Analysis & Optimization
Understanding that rigidity characteristics directly impact operational resistance, we focus on optimizing belt cross-section geometry to minimize friction while maintaining structural integrity.
Industry emphasis on rigidity alone can be misleading. Lower rigidity doesn't automatically mean lower resistance. The key factor is achieving the optimal pipe cross-section shape.
When the pipe belt approaches a perfect hexagonal cross-section, idler contact transitions from point contact within the hexagon to line contact at the hexagon edges, significantly increasing resistance despite lower rigidity values.
Optimal Belt Performance
Proper structural design and manufacturing processes create belts that maintain near-circular cross-sections under tension. This geometry ensures point contact with idlers, minimizing rolling resistance and maximizing energy efficiency throughout the system's operational life.
Suboptimal Design Consequences
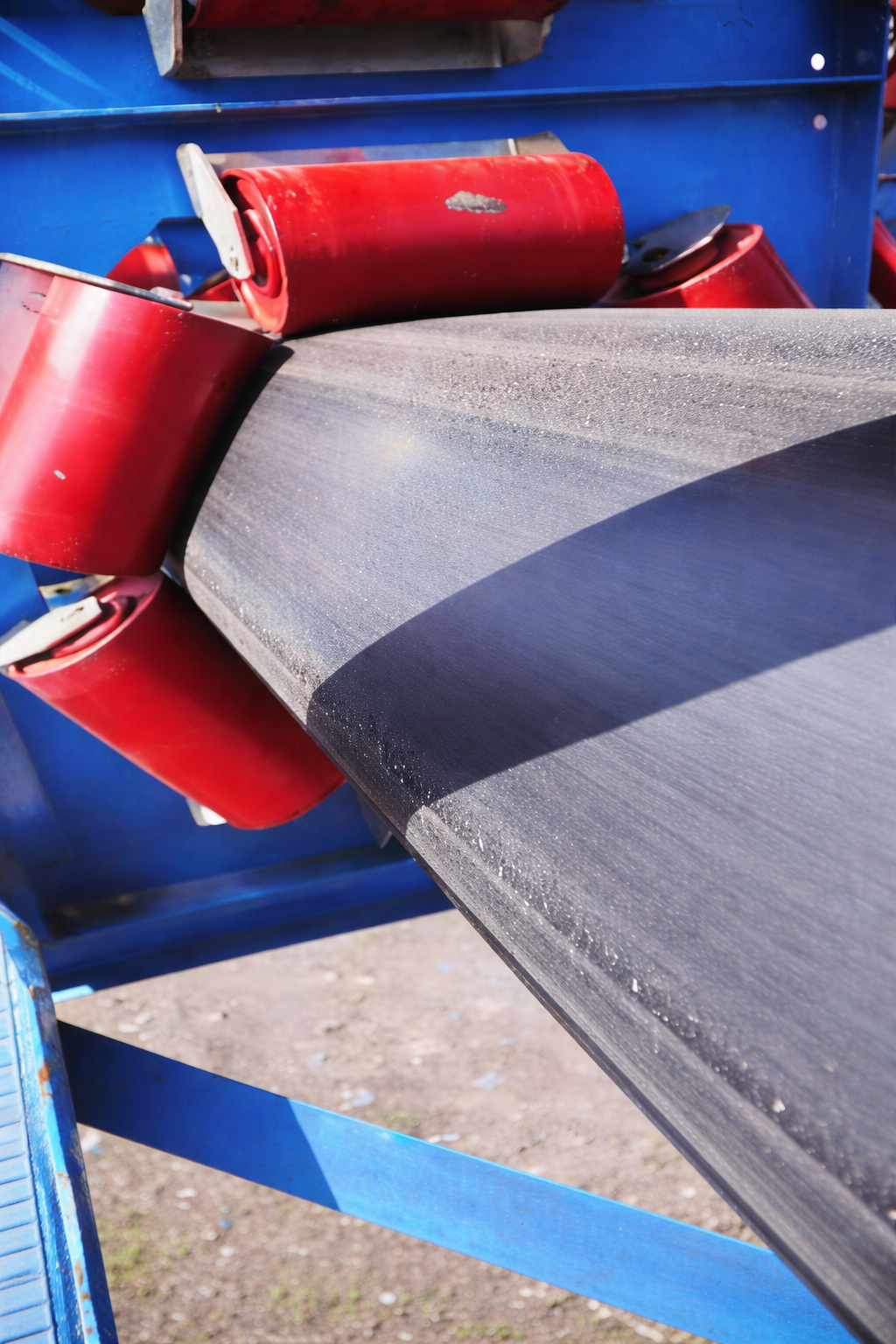

Optimize your system efficiency with properly designed pipe belt geometry
Professional Installation & Commissioning Guidelines
Proper installation and precise alignment are critical for achieving optimal performance and maximum service life from your pipe conveyor belt system. Our expert guidance ensures successful commissioning.
Proper Splice Orientation
The pipe belt splice direction must align with the horizontal transition direction to ensure superior tensile strength and buckling resistance. Standard practice uses horizontal transition and tension force direction as primary considerations for simple routing.
Sequential Belt Installation
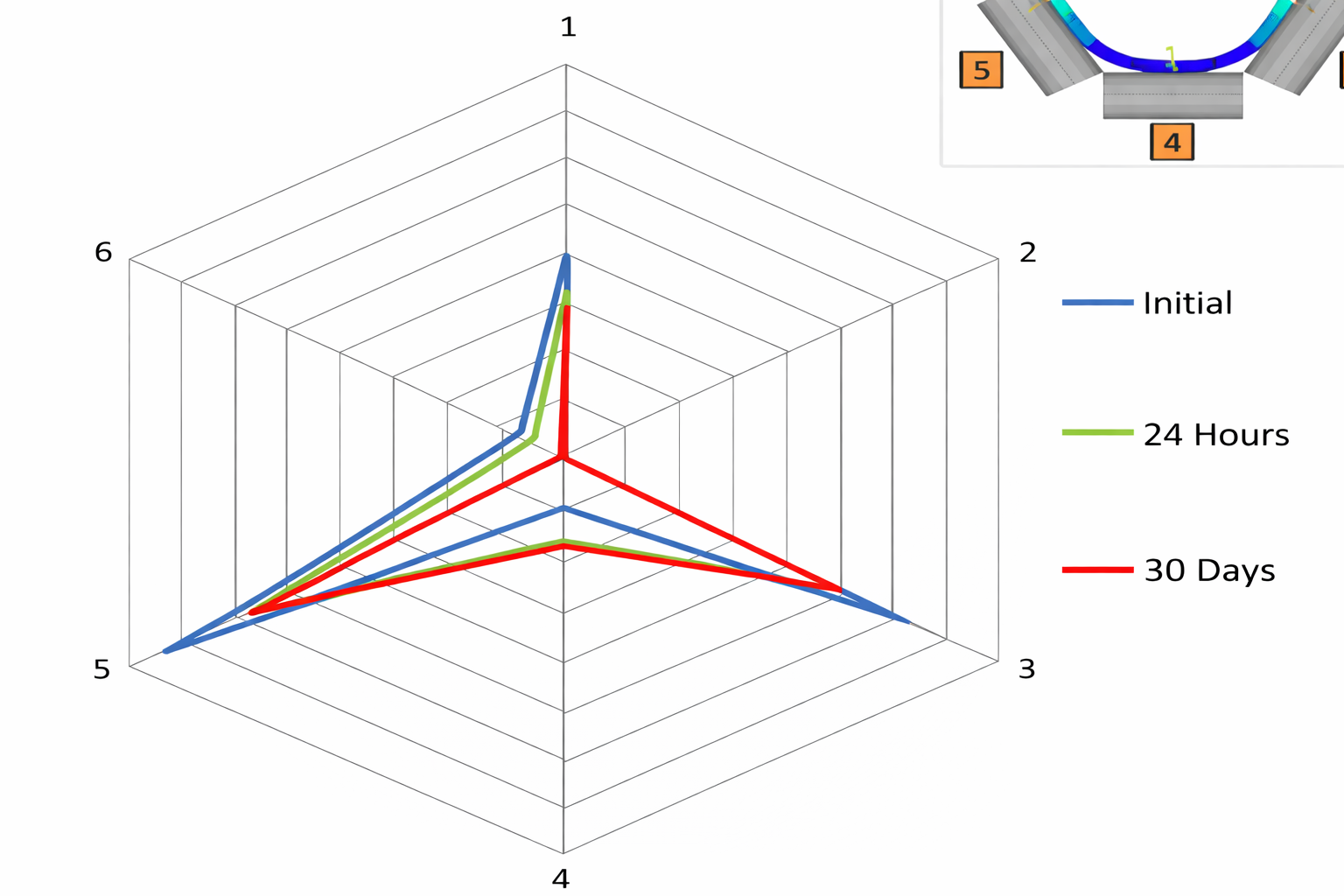
When the belt operating direction first touches the side idler, easy belt edge damage occurs. During belt operation, first contact and tension the top and bottom idlers, then contact the side idlers to prevent edge damage and ensure proper belt positioning.

Precise Belt Tracking Adjustment
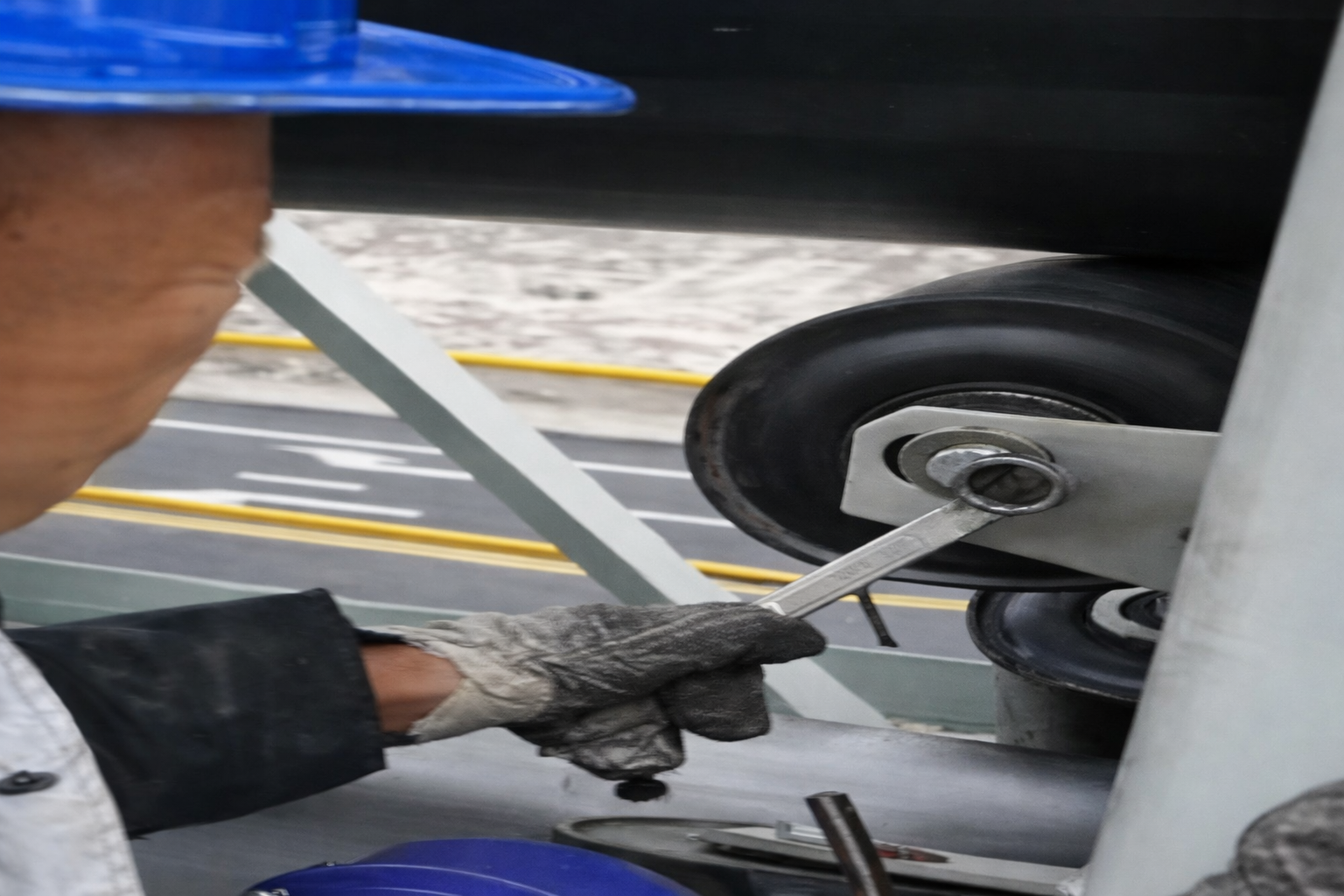
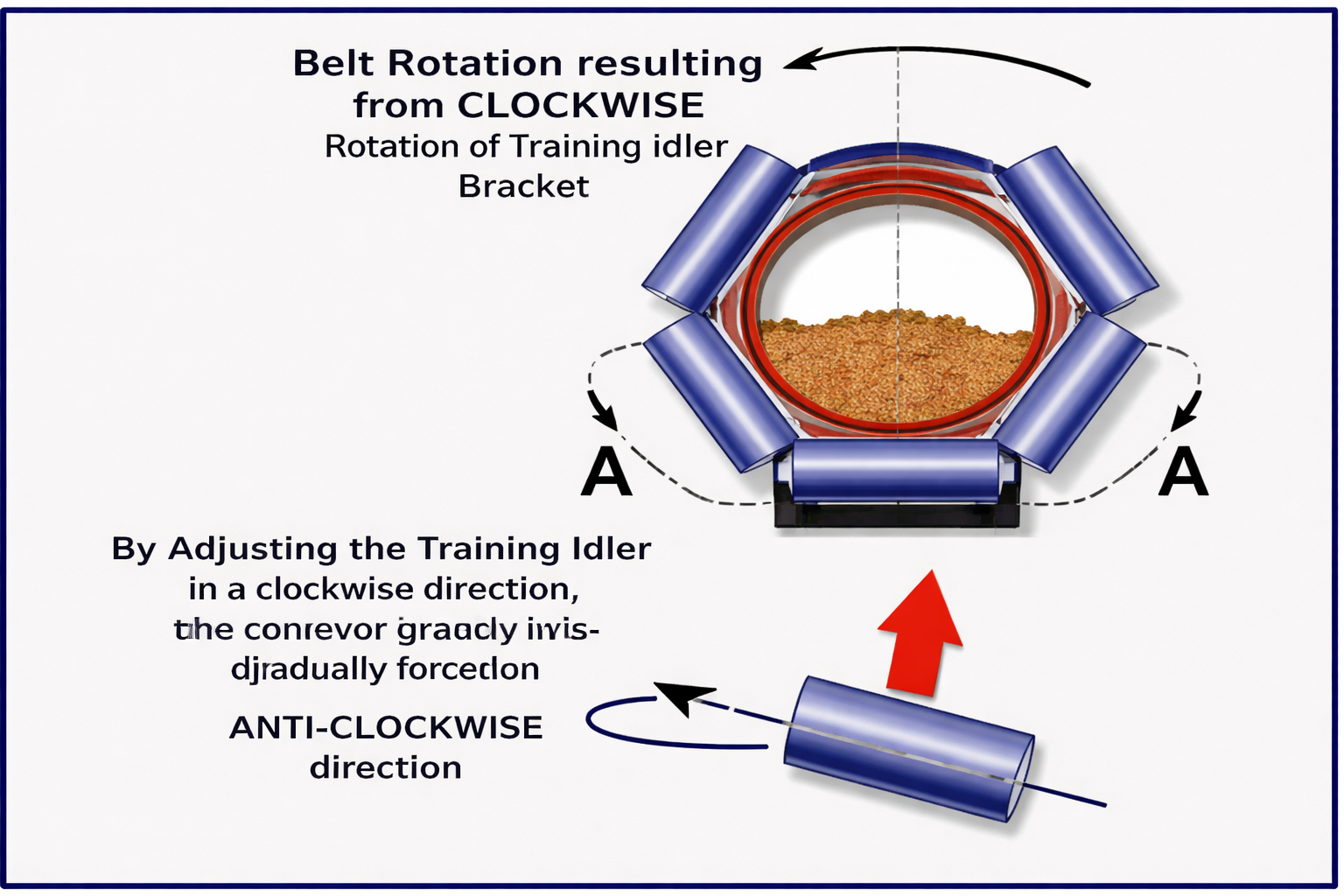
Identify where the pipe belt begins to deviate from proper alignment, then adjust the tracking idlers from that position. Fine-tune the idler orientation clockwise to gradually force the pipe conveyor to rotate counter-clockwise, correcting the deviation.

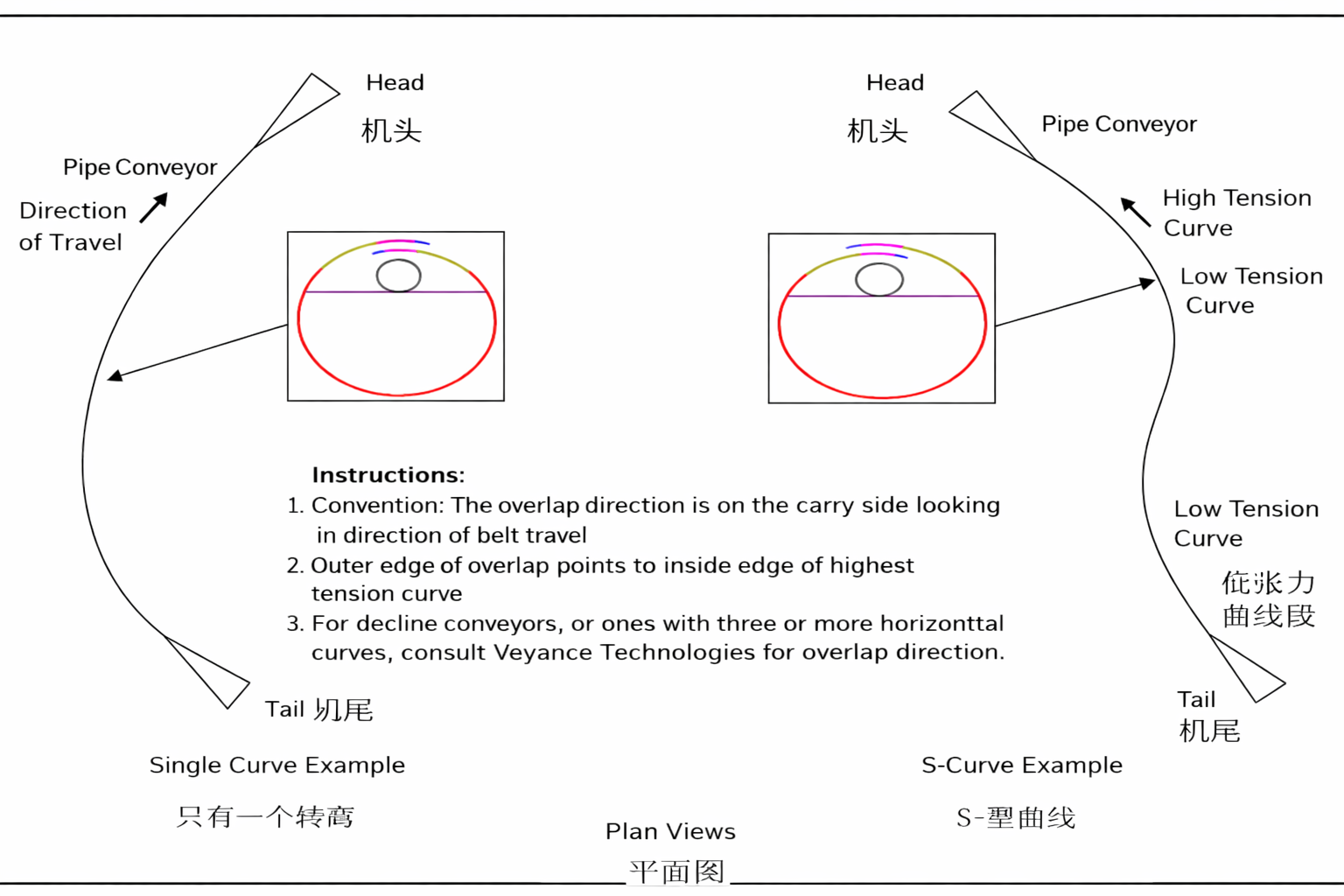
Overlap Direction Protocol
Ensure proper overlap direction aligns with material segment expectations for movement direction.
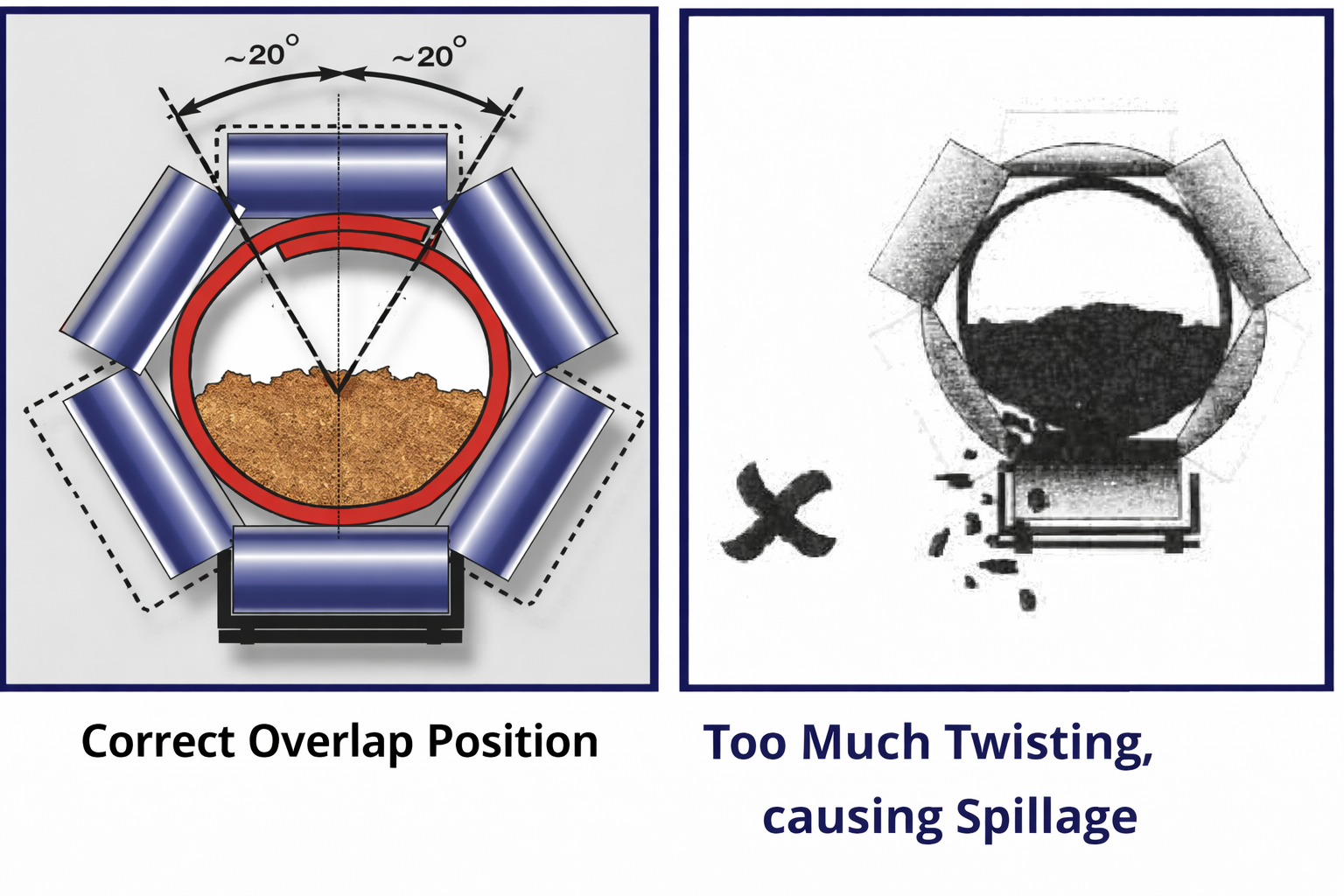
Optimal Loading Configuration
Diagram shows correct overlap positioning during carrying section loading for maximum efficiency.

Training Idler Adjustment
Detailed view of training idler clockwise adjustment mechanism for belt rotation control.
Need expert installation support for your project?
Schedule Installation TrainingCommon Failure Modes & Preventive Solutions
Learn from real-world case studies to prevent operational issues. Our comprehensive analysis identifies root causes and provides proven solutions to maximize your pipe belt system's reliability and longevity.
Primary Failure Categories During Operation
- Belt Expansion (Ballooning)
- Belt Blockage (Plugging)
- Belt Twisting (Spiraling)
- Belt Edge Damage (Abrasion)
Belt Expansion Issues
Root Cause:
Structural design problems where the pipe belt cannot maintain proper tubular shape. Poor structural design creates excessive flexibility, causing the belt to deform into a hexagonal shape that makes contact with idlers through face contact rather than the intended tangential point contact within the hexagon.

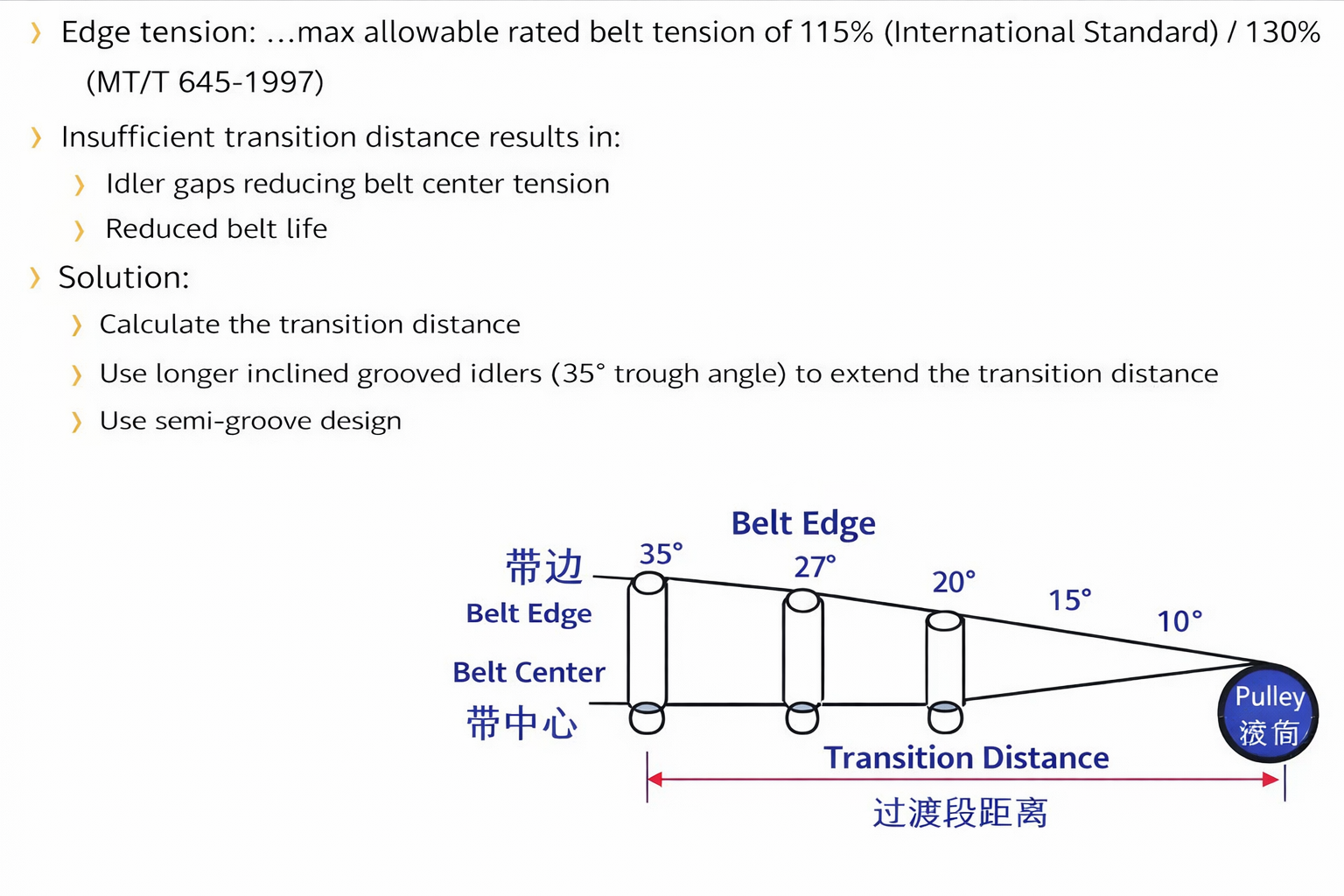
Belt Blockage Problems
Primary Causes:
• Insufficient structural rigidity in belt design
• Unreasonable pipe conveyor parameters (excessively small pulley diameter, inadequate transition length)
• Excessive edge tension exceeding 115% of nominal belt tension (International Standard) or 130% (MT/T 645-1997)
• Center tension below 0 N/mm creating free slack
Consequences:
Transition section distance deficiencies lead to improper guidance, causing belt buckling failure. Reduces service life of joints and adhesion, ultimately causing system failure and costly downtime.
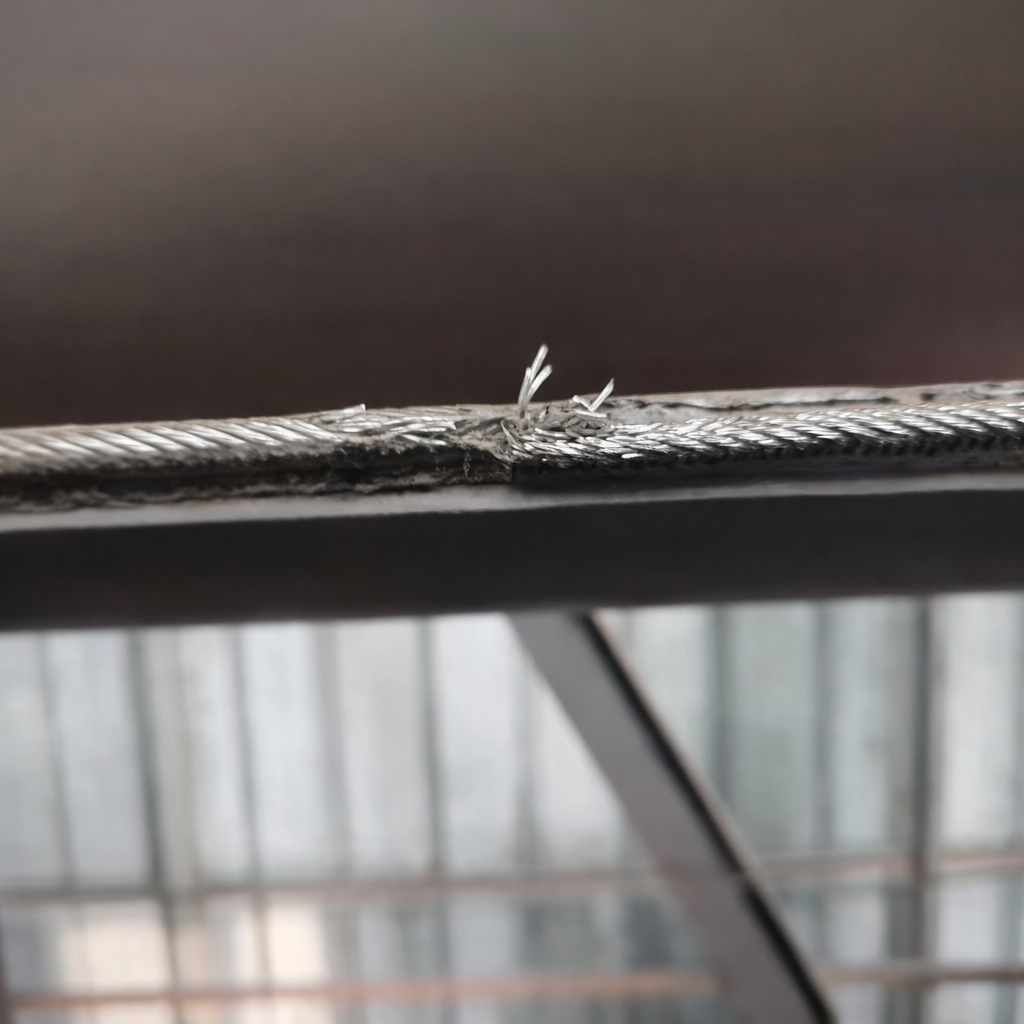
Belt Twisting Failures
Contributing Factors:
• Unreasonable structural design with poor stability - hexagonal rigidity distribution imbalance
• Improper pipe conveyor working parameters - misaligned idler group spacing causing asymmetric forces
• External environmental factors causing sudden resistance changes due to belt edge tearing, rainwater infiltration, or similar conditions
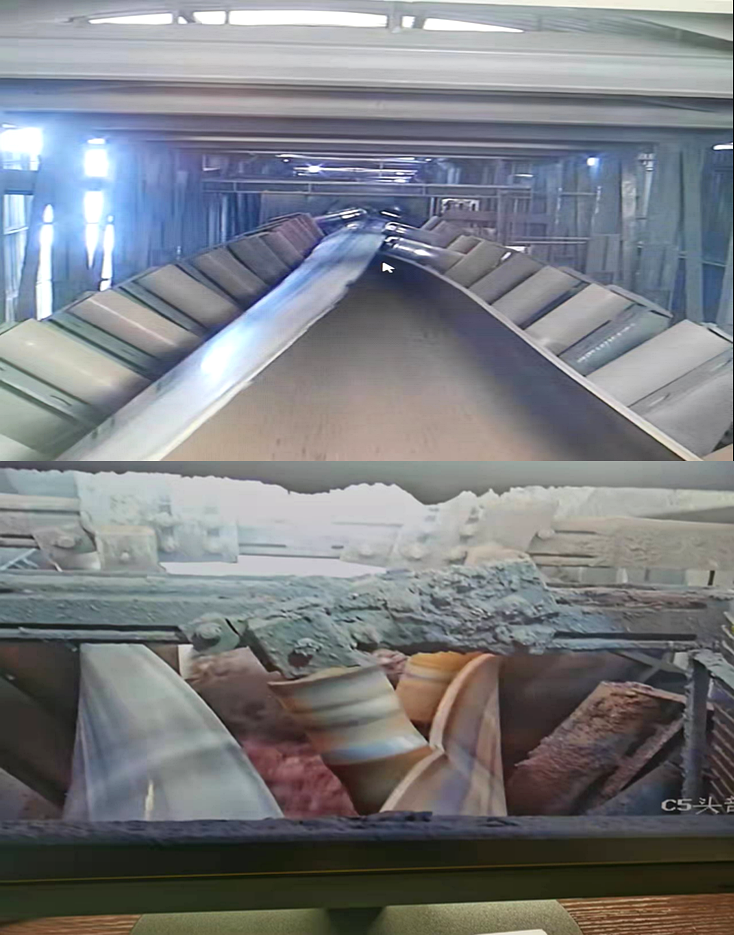

Belt Edge Damage
Mechanism:
At constant speed operation through convergence and expansion transition sections, the belt requires external force from idlers to close into tubular form at convergence. During expansion transition, idlers must apply external force to open the tube. These transition zones create high shear friction forces between idlers and belt edges, causing accelerated wear to both the belt edge and idler surfaces.
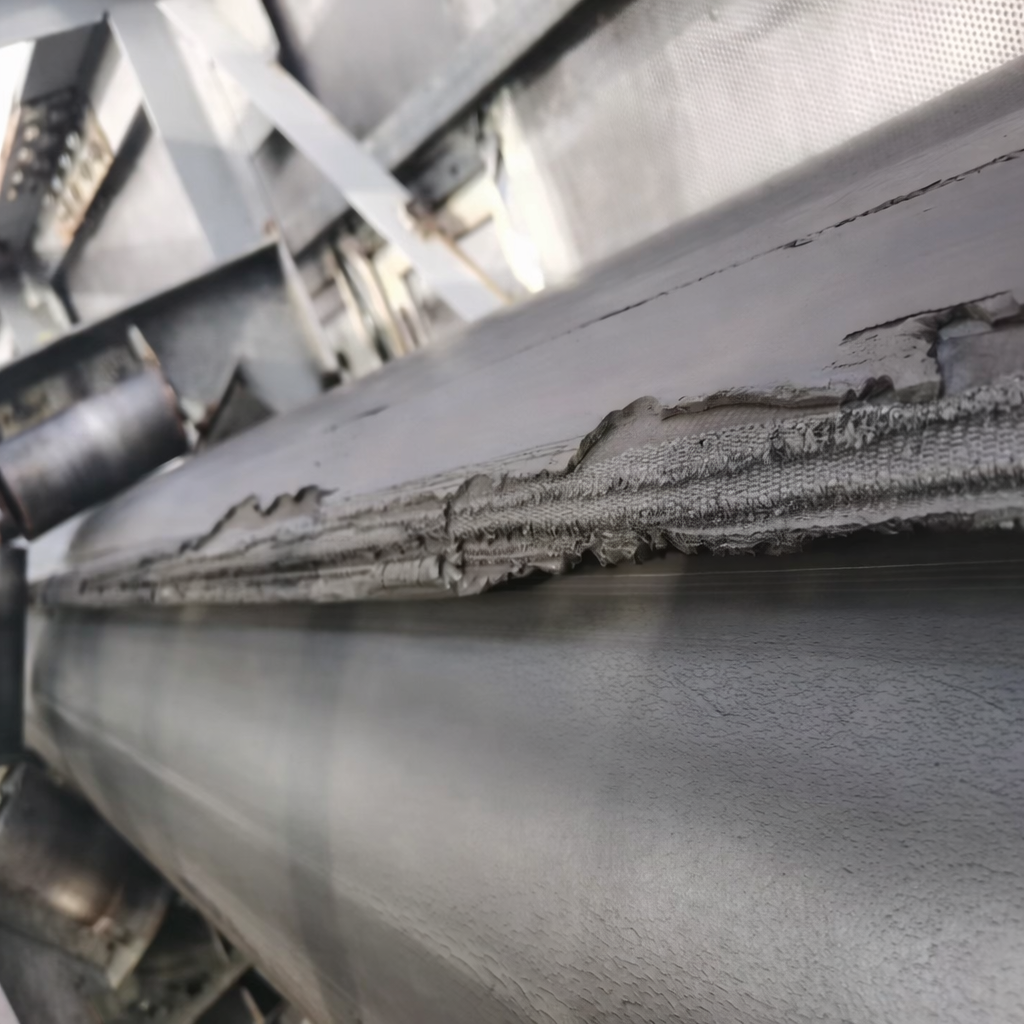


Comprehensive Prevention Strategies
Edge damage of pipe belts is a common system-wide issue. Current improvement methods focus on three key areas:
- Optimize structural design to minimize edge rigidity while maintaining overall belt strength
- Refine production processes, including forming belt edges with rounded arc profiles instead of standard corners
- Improve transition section layout and optimize idler structural design for reduced edge stress
Design Optimization Results
Our enhanced design modifications demonstrate measurable improvements:
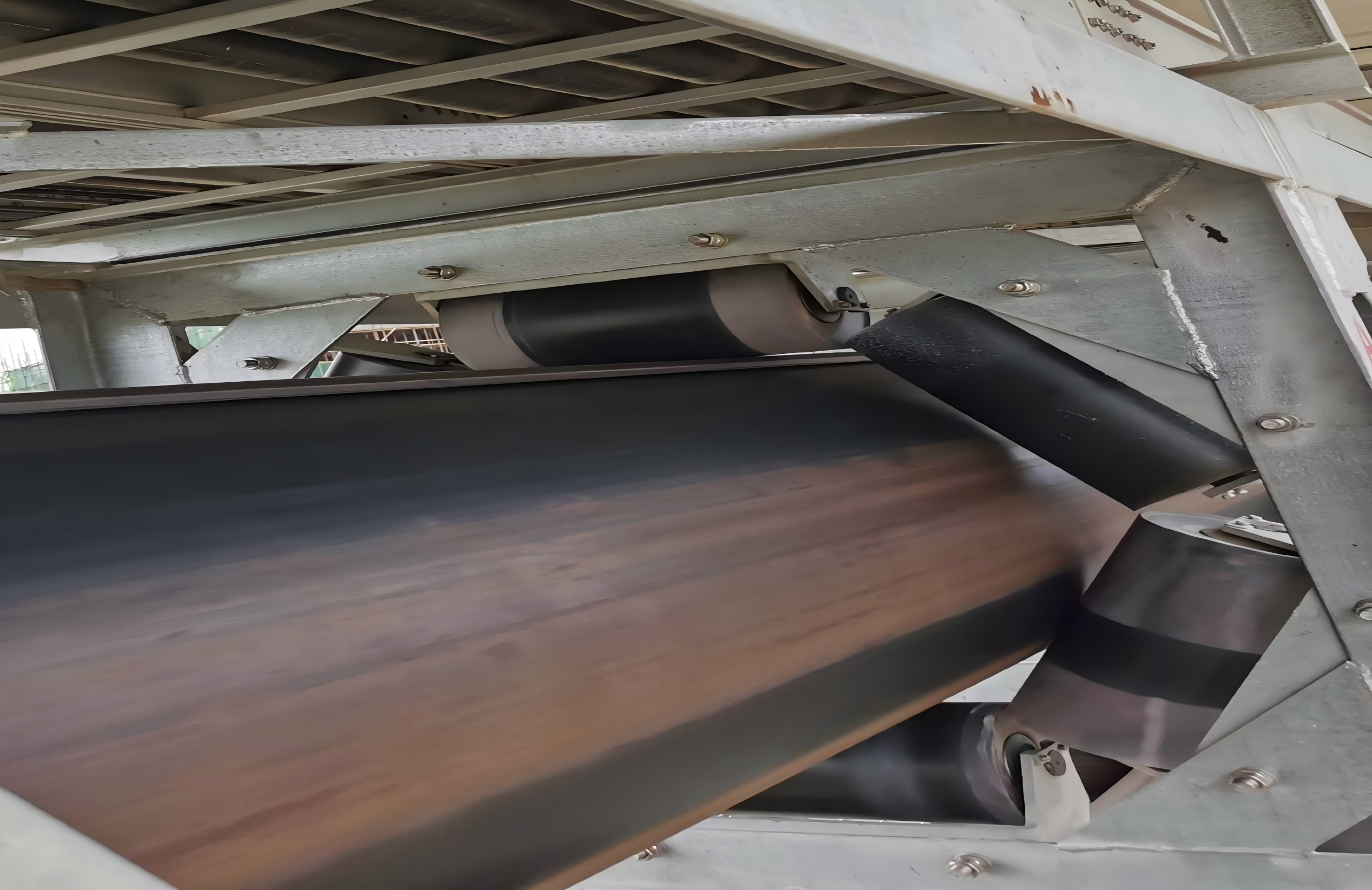

Modified Transition Idler Design
Prevent costly failures with expert engineering support
Get Failure Analysis ConsultationWhy Pipe Conveyor Belt?
Traditional flat belts create costly operational challenges. Our enclosed pipe design delivers superior performance and environmental compliance.
❌ Traditional Belt Challenges
- Dust and fine material spillage contaminates surroundings, increasing cleanup costs and regulatory risks
- Limited to 18-20° maximum incline restricts installation flexibility and requires longer conveyor routes
- Cannot navigate around obstacles or cross roads without expensive bridge structures
- Open design generates excessive noise pollution affecting worker safety and community relations
- Weather exposure damages materials and reduces belt service life
✓ Pipe Belt Advantages
- Fully enclosed tubular structure eliminates 100% of dust emissions, meeting strictest environmental standards
- Handles steep 30° inclines, reducing conveyor length by up to 40% and saving installation space
- 3D routing capability allows horizontal and vertical curves to navigate around any obstacle efficiently
- Enclosed design reduces noise by 60% compared to traditional systems, creating safer work environments
- Weather-proof protection prevents material degradation and extends belt lifetime by 30-50%
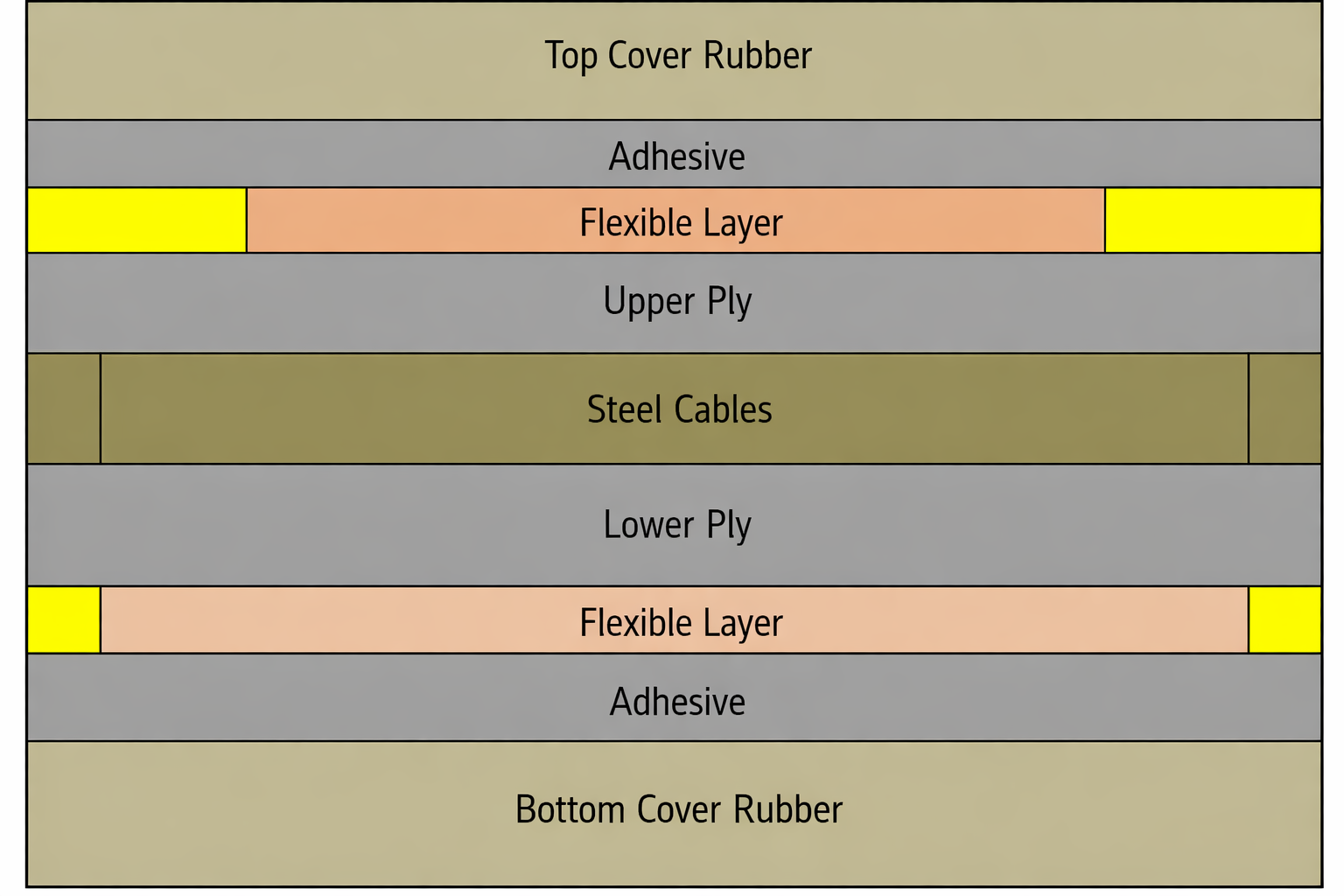
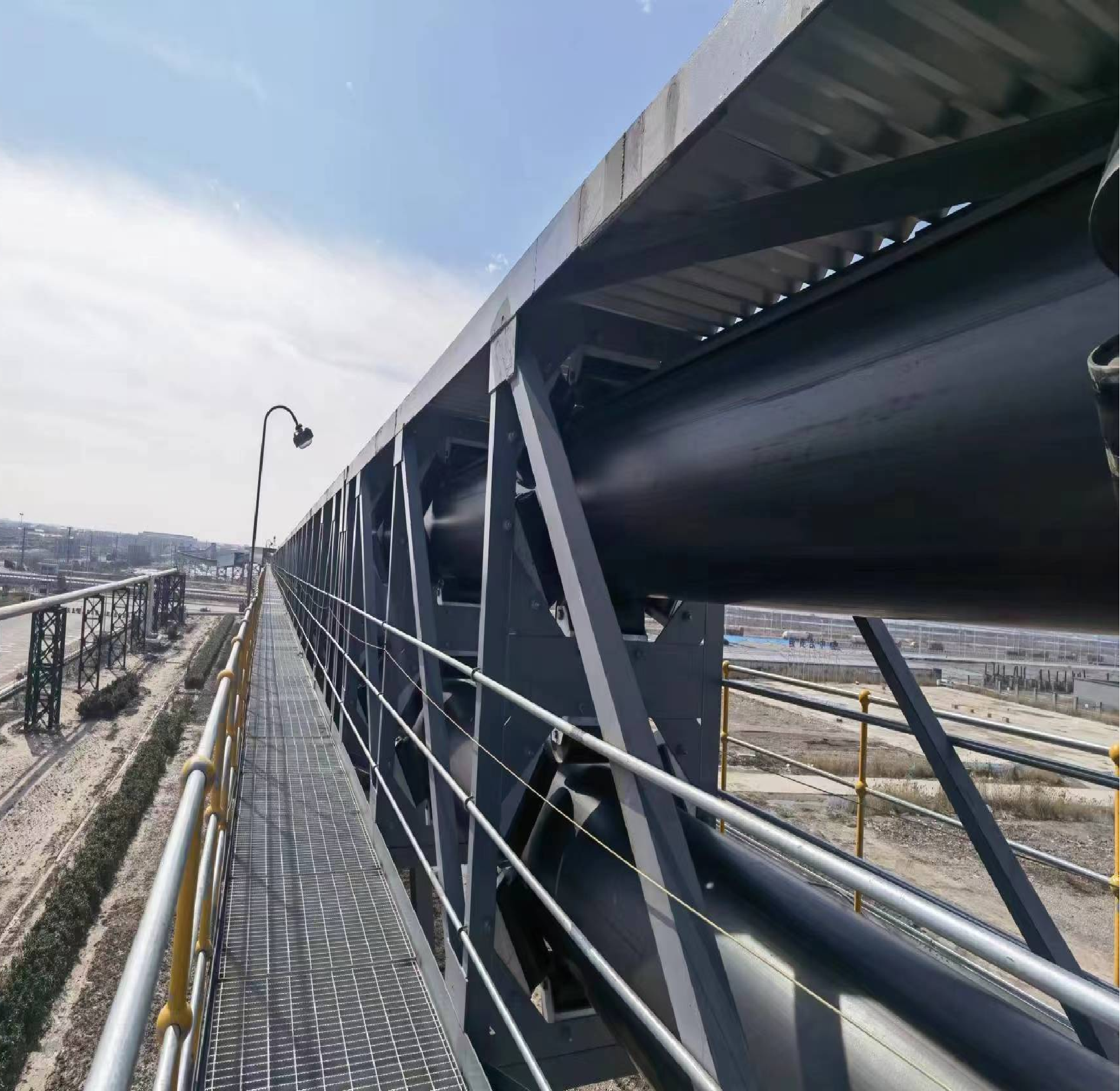
Product Structure & Key Advantages
Engineered tubular design that transforms from flat to pipe shape, providing complete material enclosure during transport
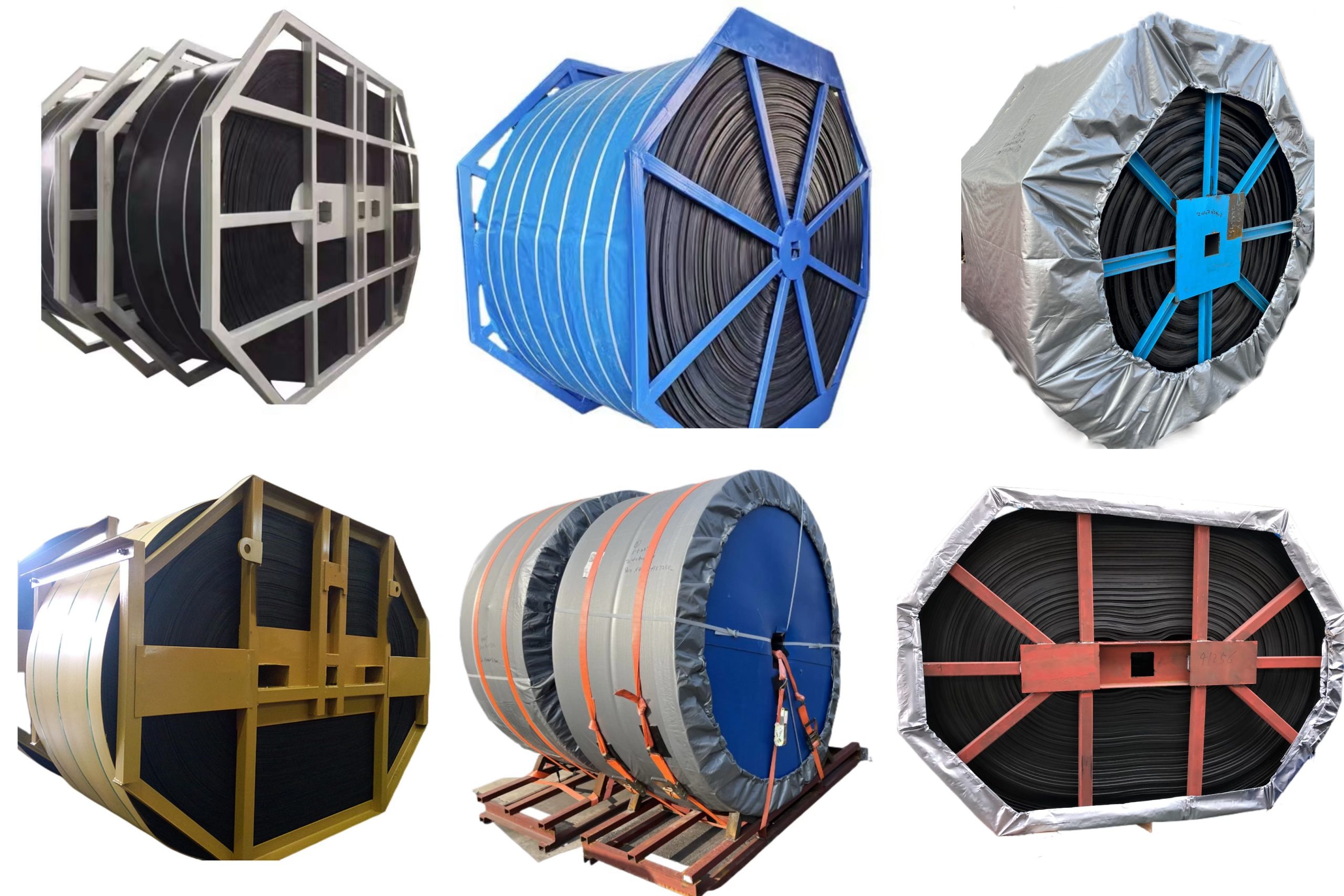

- Fully Enclosed Transport prevents material from flying, spilling or mixing with foreign substances, ensuring 100% dust-free operation that protects both your products and the environment
- Maximum 30° Incline Capability enables steeper conveying angles than traditional flat belts, reducing overall conveyor length by 40% and significantly lowering installation costs
- 3D Space Routing with horizontal and vertical curves allows flexible layout design around existing structures, perfect for complex facility configurations
- Minimal Installation Footprint requires up to 50% less space than conventional systems, maximizing valuable floor area for other operations
- 60% Noise Reduction compared to standard conveyor lines creates a safer, more comfortable working environment and improves community relations
- Lower Energy Consumption than ordinary conveyor systems reduces operating costs by 15-25% while supporting your sustainability goals
- Road Crossing Capability eliminates need for expensive bridge structures when conveyor must traverse roads or other obstacles
Technical Specifications
Comprehensive range of diameters and configurations to match your specific conveying requirements and throughput demands
Conveying Efficiency & Capacity
| Inner Pipe Diameter (mm) | Loading Area (m²) | Conveying Speed (m/min) | Conveying Volume (m³/Hr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 0.013 | 120 | 95 |
| 200 | 0.024 | 130 | 184 |
| 250 | 0.037 | 140 | 309 |
| 300 | 0.053 | 150 | 477 |
| 350 | 0.072 | 175 | 758 |
| 400 | 0.094 | 200 | 1131 |
| 500 | 0.147 | 225 | 1988 |
| 600 | 0.212 | 250 | 2875 |
| 700 | 0.289 | 275 | 3931 |
| 800 | 0.377 | 300 | 5157 |
Need help sizing your pipe conveyor system?
Contact Our EngineersStandard Specifications
Complete range of steel cord strength grades and cover configurations engineered for optimal performance in your application
| Strength Grade | Tensile Strength (KN/m) |
Cord Pitch (mm) |
Cord Diameter (mm) |
Cord Min. Breaking Force (KN) |
Cover Min. Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST-630 | 630 | 10 | 2.8 | 7.0 | 4.0 |
| ST-800 | 800 | 10 | 3.0 | 8.9 | 4.0 |
| ST-1000 | 1000 | 12 | 3.7 | 12.9 | 4.0 |
| ST-1250 | 1250 | 12 | 4.2 | 16.1 | 4.0 |
| ST-1600 | 1600 | 12 | 4.7 | 20.6 | 4.0 |
| ST-2000 | 2000 | 12 | 5.3 | 25.6 | 4.0 |
| ST-2500 | 2500 | 15 | 6.8 | 40.0 | 5.0 |
| ST-2800 | 2800 | 15 | 7.0 | 44.8 | 5.0 |
| ST-3150 | 3150 | 15 | 7.8 | 50.5 | 5.5 |
| ST-3500 | 3500 | 15 | 8.2 | 56.0 | 6.0 |
| ST-4000 | 4000 | 15 | 8.8 | 63.5 | 6.5 |
| ST-4500 | 4500 | 16 | 9.7 | 76.3 | 7.0 |
| ST-5000 | 5000 | 17 | 10.9 | 91.0 | 7.5 |
| ST-5400 | 5400 | 17 | 11.3 | 98.2 | 8.0 |
| Nominal Pipe Diameter (mm) | φ200 | φ250 | φ300 | φ350 | φ400 | φ500 | φ600 | φ700 | φ800 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width (mm) | 800 | 1000 | 1100 | 1300 | 1600 | 1850 | 2250 | 2450 | 2800 |
Don't see your required specification? We offer custom configurations!
Request Custom QuotePipe Rubber Cover Grade:
| Cover Grade | Country | Applicable Standards | Min. Tensile Strength (Mpa) |
Min. Elongation at Break (%) |
Max. Abrasion Loss (mm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN-Z | Germany | DIN22102 | 15 | 350 | 250 |
| DIN-Y | Germany | DIN22102 | 20 | 400 | 150 |
| DIN-X | Germany | DIN22102 | 25 | 450 | 120 |
| DIN-W | Germany | DIN22102 | 18 | 400 | 90 |
| RMA-I | U.S.A | RMA | 17 | 400 | 150 |
| RMA-II | U.S.A | RMA | 14 | 400 | 200 |
| ARPM RMA-I | U.S.A | ARPM | 17 | 400 | 125 |
| ARPM RMA-II | U.S.A | ARPM | 14 | 400 | 175 |
| ISO-L | International | ISO-10247 | 15 | 350 | 200 |
| ISO-H | International | ISO-10247 | 24 | 450 | 120 |
| ISO-D | International | ISO-10247 | 18 | 400 | 100 |
| AS-N | Australian | AS-1332 | 17 | 400 | 200 |
| AS-M | Australian | AS-1332 | 24 | 450 | 125 |
| AS-A | Australian | AS-1332 | 17 | 400 | 70 |
| SANS-N | South Africa | SANS-1173 | 17 | 400 | 150 |
| SANS-M | South Africa | SANS-1173 | 25 | 450 | 120 |
| SANS-A | South Africa | SANS-1173 | 18 | 400 | 70 |
| BS-M | UK | BS-490 | 24 | 450 | 120 |
| BS-N | UK | BS-490 | 17 | 400 | 200 |
| IS-N-17 | India | IS 1891 | 17 | 400 | 200 |
| IS-M-24 | India | IS 1891 | 24 | 450 | 150 |
| JIS-G | Japan | JIS-K 6332 | 14 | 400 | 250 |
| JIS-L | Japan | JIS-K 6332 | 15 | 350 | 200 |
| JIS-D | Japan | JIS-K 6332 | 18 | 400 | 100 |
| JIS-H | Japan | JIS-K 6332 | 24 | 450 | 120 |
| GB-H | China | GB/T 7984 | 24 | 450 | 120 |
| GB-D | China | GB/T 7984 | 18 | 400 | 100 |
| GB-L | China | GB/T 7984 | 15 | 350 | 200 |
Industries & Applications
Trusted by leading companies worldwide for demanding bulk material handling applications across diverse industrial sectors

Electromechanical equipment

Power Stations & Heating Facilities

steel plant

Ri Zhao Port

pier

Guoyue (Shaoguan) Power

Power Generation

Silo Conveyor Systems

China Coal Shangrao Power Plant

Garbage Incinerating Plants
See how our pipe conveyor belts can transform your operation
Schedule a Site VisitLet's Build Reliable Conveyor Solutions Together
Send us your specifications or project details — our engineers will analyze your requirements in 24h
Why Choose ZHENXING?
Contact Information
zhenxinglisa@hotmail.com
+86 18661664598
1. EP NN CC ST,SIDEWALL FR MOR HR EPDM -DONGYING
2. Solid Woven PVC PVG Conveyor Belt -JINING, Shandong
3. Sidewall Conveyor Belt -Weifang, Shandong
Get Your Custom Solution in 24 Hours
Share your requirements and receive expert guidance with a tailored quote
