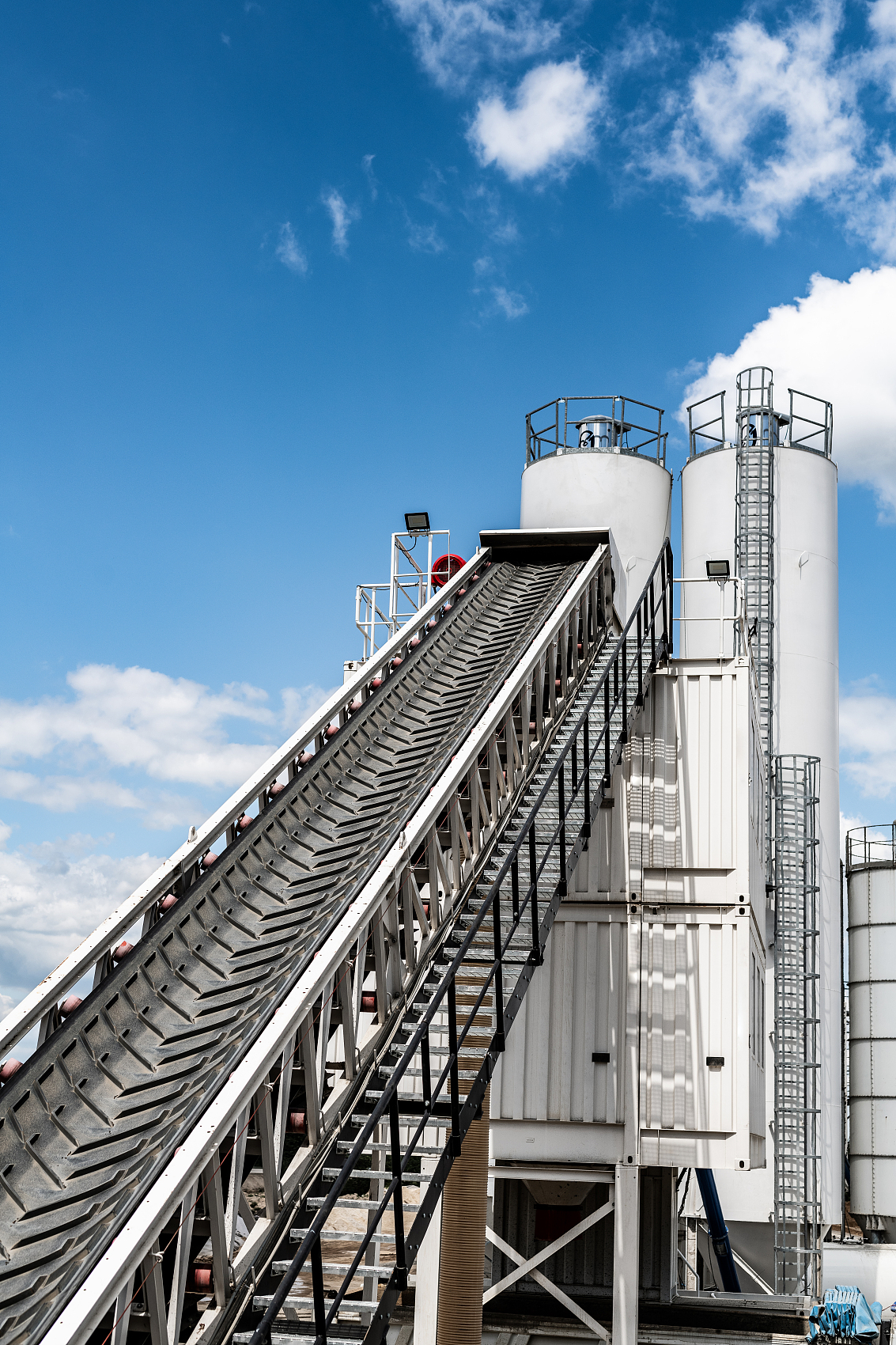
Transporting bulk materials on steep inclines often leads to product slippage, waste, and safety risks. These inefficiencies reduce output and increase cleanup costs. The solution lies in a cleated conveyor belt — designed with raised profiles that grip materials firmly, preventing rollback and ensuring smooth, efficient transport even at challenging angles. This innovation transforms incline conveying into a safe, reliable, and cost-effective process.
1. The Core Function of a Cleated Conveyor Belt
A cleated conveyor belt uses raised profiles to create pockets that hold material securely, preventing it from sliding backward during steep-incline transport. This design ensures a consistent flow of goods, which maximizes throughput and operational efficiency.

Solving Steep-Incline Conveying
By dividing the belt’s surface, cleats overcome the forces of gravity that cause material rollback on smooth belts. The bottom line is, this allows you to move products at much steeper angles, saving space and streamlining your facility layout.
- Prevents material slippage
- Enables steeper conveyor angles
- Increases overall carrying capacity
How do cleats prevent material fallback?
Cleats act as barriers, compartmentalizing bulk materials and providing the necessary support to lift them against gravity. What does this mean for you? It means less product damage, reduced spillage, and a safer work environment for your team.
- Creates pockets for loose items
- Supports the weight of the material
- Minimizes loss of product during transport
Key Takeaway: A cleated conveyor belt provides the necessary grip to move materials up inclines, preventing slippage and improving throughput.
| Feature | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Raised Cleats | Prevents material fallback and slippage. | |
| Compartments | Secures and contains bulk goods. | |
| Steep Angle Capability | Maximizes space and system efficiency. |
This fundamental design directly solves the primary challenge of incline conveying.
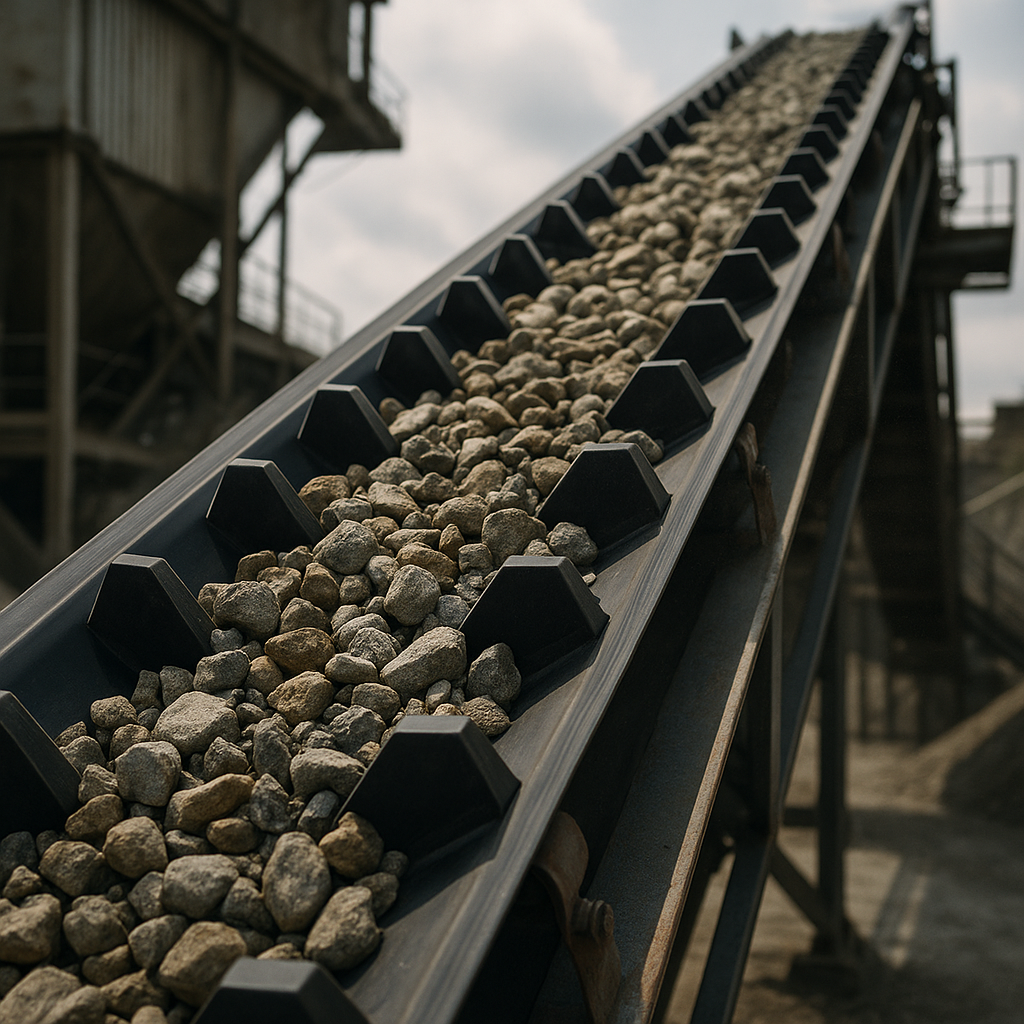
2. Cleated Conveyor Belt Vulcanization Methods
The manufacturing process, known as vulcanization, permanently bonds the cleats to the base belt either after the belt is cured (post-vulcanized) or during the same curing process (co-vulcanized). Each method produces cleats with distinct properties suited for different operational demands.
Post-Vulcanized vs. Co-Vulcanized
Post-vulcanized cleats are made from a hard, wear-resistant rubber compound and are attached to a fully cured belt. Here’s the deal: co-vulcanized cleats are formed from the same material as the top cover and cured simultaneously, creating a single, seamless piece.
- Post-Vulcanized: Harder, separate cleat.
- Co-Vulcanized: Softer, integrated cleat.
Impact on Flexibility and Durability
Post-vulcanized cleats offer superior durability for heavy-duty applications, while co-vulcanized belts provide greater flexibility. You might be wondering why this matters. The belt’s flexibility impacts its ability to wrap around smaller pulleys without stress or damage.
- Durability: Post-vulcanized for abrasive materials.
- Flexibility: Co-vulcanized for smaller pulleys.
Key Takeaway: The vulcanization method determines the belt’s flexibility, durability, and ideal use case.
| Method | Cleat Hardness | Belt Flexibility | Best For | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Vulcanized | High | Lower | Heavy-duty, abrasive materials | |
| Co-Vulcanized | Lower | Higher | Small pulleys, delicate goods |
This choice directly influences the belt’s performance and compatibility with your conveyor system.
3. Post-Vulcanized Cleated Conveyor Belt Details
A post-vulcanized (or subsequently vulcanized) cleated conveyor belt features extremely robust, wear-resistant cleats that are bonded onto the base belt in a secondary process. These cleats are ideal for handling abrasive and heavy bulk materials.

Properties of Subsequently Vulcanized Cleats
These cleats are known for their exceptional hardness and resistance to wear and tear from rough materials. Here’s the deal: their sturdy construction ensures a long service life even in the toughest conditions.
- High abrasion resistance
- Available in heights up to 50 mm
- Excellent for heavy bulk goods
When should I choose a post-vulcanized belt?
You should opt for a post-vulcanized belt when your application involves conveying heavy, sharp, or abrasive materials like gravel, coal, or scrap metal. What does this mean for you? It means you get a durable solution that withstands harsh use without frequent replacement.
- Mining and quarrying
- Recycling facilities
- Heavy construction material transport
Key Takeaway: Post-vulcanized cleated belts offer robust, wear-resistant profiles ideal for heavy-duty applications.
| Property | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|
| High Hardness | Superior wear resistance. | |
| Tall Profiles | Increased carrying capacity for large materials. | |
| Strong Bond | Reliable performance under heavy loads. |
This belt type is the workhorse for the most demanding incline conveying tasks.
4. Co-Vulcanized Cleated Conveyor Belt Details
A co-vulcanized cleated conveyor belt is manufactured in a single process where the cleats and the belt cover are cured together, forming one seamless unit. This results in a highly flexible belt with softer profiles.
Advantages of Simultaneous Vulcanization
The primary advantage is the exceptional flexibility, which allows the belt to run smoothly over smaller pulleys without cracking or delamination. You might be wondering about the benefit. This flexibility enables more compact and energy-efficient system designs.
- Superior troughability
- Compatible with small pulley diameters
- Excellent flex life
Why does this belt have a self-cleaning effect?
The softer, integrated profiles flex as the belt moves around pulleys, which helps dislodge any sticky material that might otherwise build up. The bottom line is this natural movement reduces cleaning needs and prevents caking.
- Reduces material buildup
- Lowers maintenance downtime
- Maintains consistent carrying capacity
Key Takeaway: Co-vulcanized belts feature softer, integrated profiles, enhancing flexibility and self-cleaning.
| Feature | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|
| High Flexibility | Suitable for compact systems with small pulleys. | |
| Integrated Profile | No risk of cleat separation. | |
| Self-Cleaning | Reduces maintenance and ensures consistent flow. |
This integrated design promotes system efficiency and reduces operational burdens.
5. Choosing Your Cleated Conveyor Belt Profile
Selecting the right profile involves matching the cleat’s design, height, and spacing to the specific characteristics of the material you are conveying. This decision is critical for ensuring optimal performance and preventing spillage.
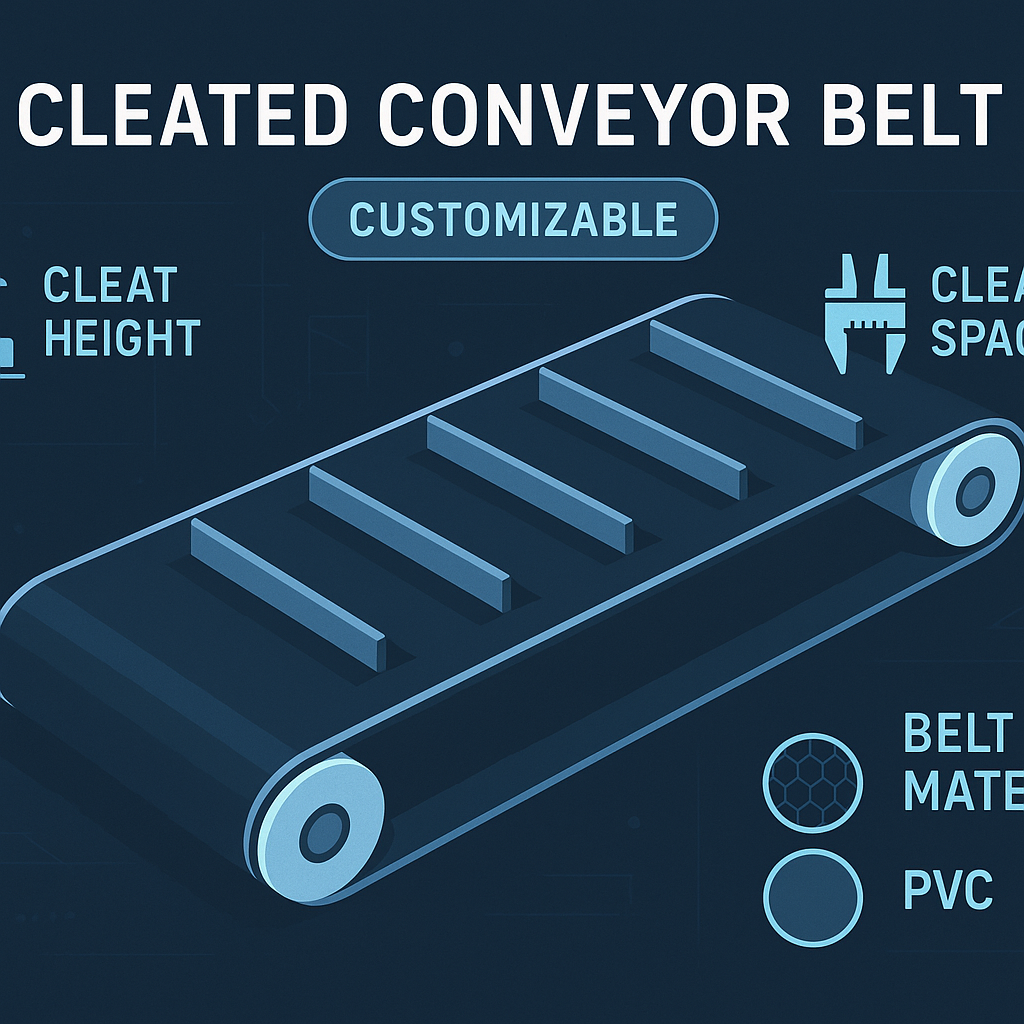
Understanding Cleat Design and Spacing
The shape of the cleat (e.g., T-shape, V-shape) and the distance between them must suit the size and flowability of your material. Let’s dig a little deeper. Proper spacing ensures that material is picked up effectively without overloading the belt.
- V-shapes for better troughing
- Straight cleats for uniform products
- Spacing based on material lump size
How does cleat height affect carrying capacity?
Taller cleats create deeper pockets, allowing you to carry a larger volume of material per foot of the belt, especially on steep inclines. What does this mean for you? Choosing the correct height directly increases your system’s throughput and efficiency.
- Taller cleats for larger lump sizes
- Lower cleats for fine or packaged goods
- Height determines volumetric capacity
Key Takeaway: Selecting the correct cleat design, height, and spacing is critical for optimizing material transport.
| Parameter | Influences | |
|---|---|---|
| Cleat Height | Carrying capacity and material size. | |
| Cleat Spacing | Material pickup and belt load. | |
| Cleat Shape | Troughability and material type. |
Careful specification of these parameters is key to a successful implementation.
6. A Cleated Conveyor Belt for Special Materials
Specialized cleated conveyor belts are engineered with unique rubber compounds and profiles to handle challenging materials that are hot, oily, or delicate. Standard belts would quickly degrade or fail in these conditions.

Transporting Hot, Oily, or Greasy Goods
These belts use compounds that are resistant to heat, oil, and grease, preventing the rubber from swelling, cracking, or losing integrity. Here’s the deal: this ensures a safe and reliable operation when conveying challenging substances.
- Heat-resistant compounds
- Oil- and grease-resistant materials
- Flame-retardant options available
What makes a belt suitable for special materials?
Suitability comes from a combination of a specially formulated cover compound and a cleat design that won’t damage the product. The bottom line is, you get a belt that not only moves your product but also protects its quality.
- Non-marking compounds for delicate items
- Food-grade materials
- Chemical-resistant formulations
Key Takeaway: Specialized cleated belts use unique compounds and profiles designed for challenging materials.
| Material Challenge | Belt Solution | |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperatures | Heat-resistant rubber compound. | |
| Oils & Greases | Oil-resistant (OR) cover. | |
| Delicate Products | Soft, non-marking profiles. |
Using the right specialty belt extends its service life and protects your product.
7. Cleated Conveyor Belt and Pulley Dynamics
The relationship between a cleated conveyor belt and the conveyor’s pulleys is defined by the belt’s flexibility, which dictates the smallest pulley diameter it can safely wrap around. Ignoring this can lead to premature belt failure.

Minimum Pulley Diameter Explained
The minimum pulley diameter is the smallest size a belt can travel around without causing stress cracks in the cleat base or cover. You might be wondering why this is crucial. Adhering to this specification prevents belt damage and ensures longevity.
- Co-vulcanized belts allow smaller pulleys
- Post-vulcanized belts require larger pulleys
- Prevents stress-related damage
Will cleated belts work with my existing pulleys?
Whether a cleated belt will work depends on if your existing pulley diameters meet the minimum requirements for the chosen belt type. Let’s dig a little deeper. Co-vulcanized belts are often a better fit for retrofitting systems with smaller pulleys.
- Check manufacturer specifications
- Measure your drive and tail pulleys
- Consider belt flexibility in your choice
Key Takeaway: A belt’s flexibility, influenced by its vulcanization, directly impacts the minimum required pulley diameter.
| Belt Type | Flexibility | Minimum Pulley Diameter | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Vulcanized | High | Smaller | |
| Post-Vulcanized | Low | Larger |
Matching your belt to your pulley system is essential for operational safety and reliability.
8. The Durable Cleated Conveyor Belt Carcass
The carcass is the internal fabric or steel cord reinforcement that provides the belt with its tensile strength and structural integrity. It’s the backbone of your cleated conveyor belt, responsible for handling the tension and load of the entire system.

Textile vs. Steel Cord Reinforcement
Textile carcasses, typically made of polyester and nylon (EP), offer excellent flexibility and are suitable for most applications. Here’s the deal: steel cord carcasses provide superior strength and low elongation for long, high-tension conveyors.
- Textile (EP): Flexible, impact-resistant.
- Steel Cord: High strength, low stretch.
Why choose a steel cord carcass?
You should choose a steel cord carcass for extremely demanding jobs that involve very long distances, heavy loads, or high-lift requirements. What does this mean for you? It provides maximum stability and strength where textile belts would fail.
- Long overland conveyor systems
- High-tension incline lifts
- Heavy-duty mining operations
Key Takeaway: The belt’s internal carcass, available in textile or steel cord, provides fundamental strength for specific application stresses.
| Carcass Type | Primary Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Textile (EP) | Versatility and impact resistance. | |
| Steel Cord | Maximum tensile strength and stability. |
The right carcass ensures your belt can withstand the mechanical forces of your operation.
9. A Cleated Conveyor Belt Reduces Maintenance
A properly selected cleated conveyor belt can significantly lower maintenance needs by minimizing material spillage and, in some cases, by cleaning itself. This leads to less downtime for cleanup and repairs, boosting overall productivity.
The Self-Cleaning Effect of Soft Profiles
Co-vulcanized belts with soft, flexible cleats naturally shed sticky material as they bend around pulleys. You might be wondering how. This flexing action breaks up and dislodges residue, preventing it from caking onto the belt surface.
- Reduces material buildup
- Ensures consistent cleat performance
- Minimizes need for manual scraping
How can a belt design lower cleaning costs?
By preventing material fallback and offering a self-cleaning effect, the right belt design drastically reduces the labor and downtime associated with spillage cleanup. The bottom line is, your operational costs decrease while your uptime increases.
- Less spillage to clean under the conveyor
- Less caked-on material to remove
- Fewer production stops for maintenance
Key Takeaway: Certain cleated belt designs, particularly co-vulcanized ones, reduce material buildup, leading to less downtime.
| Feature | Maintenance Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Effective Cleats | Reduced spillage and cleanup. | |
| Flexible Profiles | Self-cleaning effect reduces caking. | |
| Durable Construction | Less frequent repairs and replacement. |
This translates directly to a better return on investment through lower operational overhead.
10. Industries Using a Cleated Conveyor Belt
The cleated conveyor belt is a versatile workhorse found across numerous industries that need to move bulk materials or individual products up an incline. Its adaptability makes it a go-to solution for a wide range of material handling challenges.
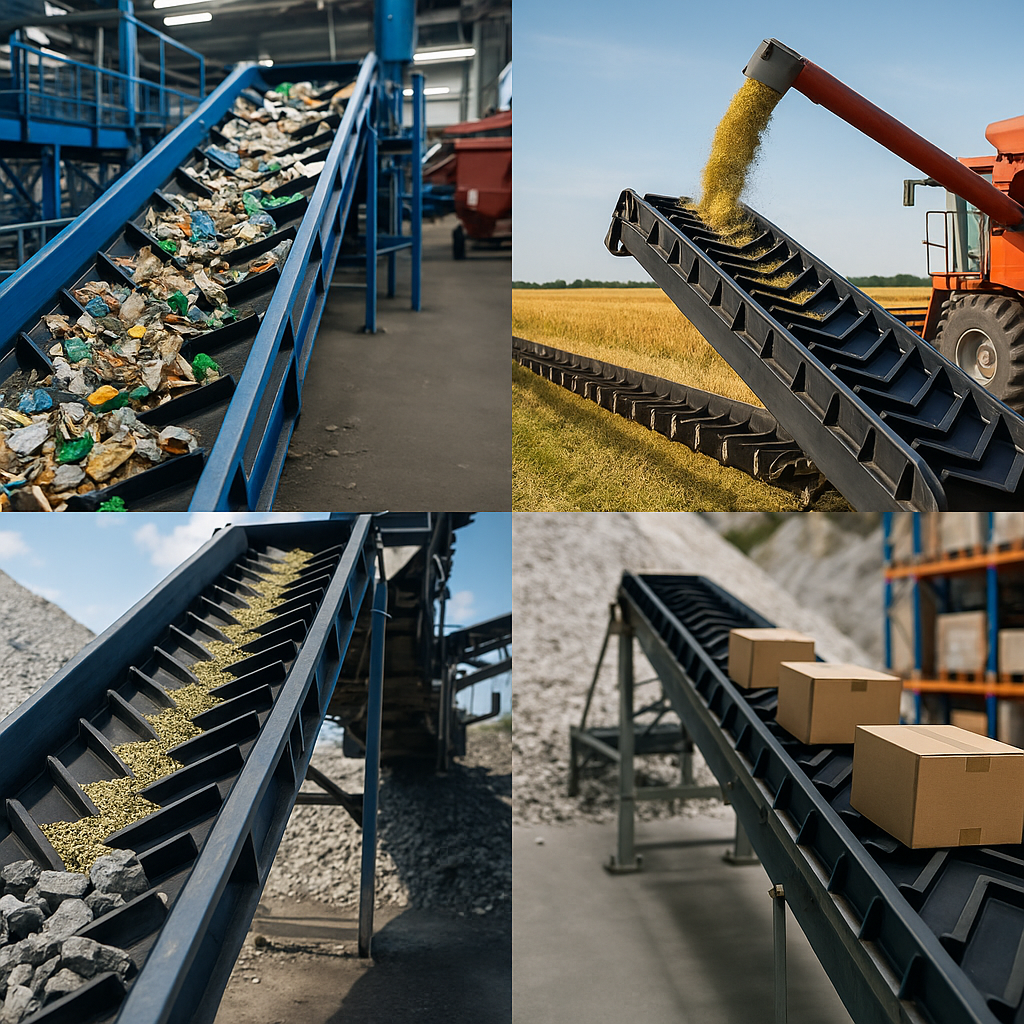

Bulk Goods and Material Handling
From recycling plants sorting plastics to quarries moving gravel, cleated belts are essential for elevating loose materials efficiently. The bottom line is they prevent the chaos of material avalanches on steep routes.
- Recycling and waste management
- Sand, gravel, and cement production
- Wood chips and sawdust handling
Can this belt be used for food processing?
Yes, cleated belts made with food-grade compounds are widely used for transporting everything from fresh produce to packaged snacks. Here’s the deal: these belts comply with safety standards and are designed for hygienic operation.
- Transporting vegetables and fruits
- Handling packaged food items
- Elevating grain and other agricultural products
Key Takeaway: From agriculture to mining, the cleated conveyor belt is a versatile solution for inclined movement of goods.
| Industry | Common Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Grain, feed, and harvested crops. | |
| Mining/Construction | Gravel, coal, sand, and cement. | |
| Recycling | Plastic, paper, and metal scrap. | |
| Food Processing | Fresh produce, packaged goods. |
Its wide range of applications highlights its essential role in modern industry.
Conclusion
Stop letting material slippage, product damage, and constant cleanup dictate your productivity. A cleated conveyor belt is the definitive solution for mastering steep-incline transport, ensuring your materials move smoothly, safely, and efficiently. We specialize in analyzing your unique operational challenges to deliver a tailored conveyor belt solution that enhances throughput, reduces maintenance, and maximizes your return on investment. Our vision is to power your progress by engineering conveying solutions that turn your steepest challenges into your greatest operational strengths.
Contact our specialists today to find the perfect cleated conveyor belt for your steep-incline needs!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I use a cleated belt for very steep angles?Yes, depending on the material and cleat design, these belts can often handle inclines up to 40 degrees or more, far exceeding the capabilities of a smooth-surface belt.
2. How do I choose the right cleat height for my material?Generally, the cleat height should be selected based on the lump size and flow characteristics of your material; taller cleats are for larger materials, while shorter ones work well for fine powders or small packages.
3. Are food-grade cleated conveyor belts available?Absolutely. Belts made from FDA-compliant materials are available for applications where the belt will come into direct contact with food products, ensuring hygienic transport.
4. Will a cleated belt damage delicate products?Not if you choose the right one. Co-vulcanized belts with soft, flexible profiles are specifically designed to handle delicate items like packaged goods or fresh produce without causing damage.
5. Can I repair a damaged cleat?It depends on the belt type and extent of the damage. While some minor repairs on post-vulcanized cleats may be possible, significant damage often requires replacing the belt section to ensure structural integrity and safety.

